A new allele conferring resistance to Lysinibacillus sphaericus is detected in low frequency in Culex quinquefasciatus field populations
- PMID: 26846600
- PMCID: PMC4743420
- DOI: 10.1186/s13071-016-1347-2
A new allele conferring resistance to Lysinibacillus sphaericus is detected in low frequency in Culex quinquefasciatus field populations
Abstract
Background: The Cqm1 α-glucosidase of Culex quinquefasciatus larvae acts as the midgut receptor for the binary toxin of the biolarvicide Lysinibacillus sphaericus. Mutations within the cqm1 gene can code for aberrant polypeptides that can no longer be properly expressed or bind to the toxin, leading to insect resistance. The cqm1 REC and cqm1 REC-2 alleles were identified in a laboratory selected colony and both displayed mutations that lead to equivalent phenotypes of refractoriness to L. sphaericus. cqm1 REC was first identified as the major resistance allele in this colony but it was subsequently replaced by cqm1 REC-2 , suggesting the better adaptive features of the second allele. The major aim of this study was to evaluate the occurrence of cqm1 REC-2 and track its origin in field populations where cqm1 REC was previously identified.
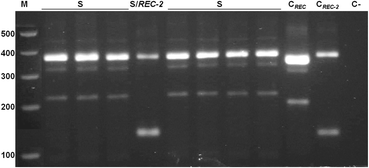
Methods: The screening of the cqm1 REC-2 allele was based on more than 2000 C. quinquefasciatus larvae from five localities in the city of Recife, Brazil and used a multiplex PCR assay that is also able to identify cqm1 REC . Full-length sequencing of the cqm1 REC-2 and selected cqm1 samples was performed to identify further polymorphisms between these alleles.
Results: The cqm1 REC-2 allele was found in field samples, specifically in two heterozygous individuals from a single locality with an overall frequency and distribution much lower than that observed for cqm1 REC . The full-length sequences from these two cqm1 REC-2 copies were almost identical to the cqm1 REC-2 derived from the resistant colony but displayed more than 30 SNPs when compared with cqm1 and cqm1 REC . The cqm1 REC and cqm1 REC-2 resistant alleles were found to be associated with two distinct sets of wild-type cqm1 variants found in field populations.
Conclusions: The cqm1 REC-2 allele occurs in populations in Recife and was probably already present in the samples used to establish the laboratory resistant colony. The data generated indicates that cqm1 REC-2 can be selected in field populations, although its low frequency and distribution in Recife suggest that cqm1 REC-2 presents a lower risk of selection compared to cqm1 REC .
Figures


Similar articles
-
Detection of an allele conferring resistance to Bacillus sphaericus binary toxin in Culex quinquefasciatus populations by molecular screening.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2009 Feb;75(4):1044-9. doi: 10.1128/AEM.02032-08. Epub 2008 Dec 19. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2009. PMID: 19098223 Free PMC article.
-
Co-selection and replacement of resistance alleles to Lysinibacillus sphaericus in a Culex quinquefasciatus colony.FEBS J. 2015 Sep;282(18):3592-602. doi: 10.1111/febs.13364. Epub 2015 Jul 20. FEBS J. 2015. PMID: 26131741
-
Novel mutations associated with resistance to Bacillus sphaericus in a polymorphic region of the Culex quinquefasciatus cqm1 gene.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2012 Sep;78(17):6321-6. doi: 10.1128/AEM.01199-12. Epub 2012 Jul 6. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2012. PMID: 22773633 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular and biological features of Culex quinquefasciatus homozygous larvae for two cqm1 alleles that confer resistance to Lysinibacillus sphaericus larvicides.Pest Manag Sci. 2021 Jul;77(7):3135-3144. doi: 10.1002/ps.6349. Epub 2021 Mar 13. Pest Manag Sci. 2021. PMID: 33644981
-
Mosquito-larvicidal Binary (BinA/B) proteins for mosquito control programs -advancements, challenges, and possibilities.Curr Res Insect Sci. 2021 Dec 18;2:100028. doi: 10.1016/j.cris.2021.100028. eCollection 2022. Curr Res Insect Sci. 2021. PMID: 36003274 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Evaluation of a long-lasting microbial larvicide against Culex quinquefasciatus and Aedes aegypti under laboratory and a semi-field trial.Parasit Vectors. 2024 Sep 14;17(1):391. doi: 10.1186/s13071-024-06465-5. Parasit Vectors. 2024. PMID: 39272177 Free PMC article.
-
Bacterial Toxins Active against Mosquitoes: Mode of Action and Resistance.Toxins (Basel). 2021 Jul 27;13(8):523. doi: 10.3390/toxins13080523. Toxins (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34437394 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Insecticide resistance in Culex quinquefasciatus Say, 1823 in Brazil: a review.Parasit Vectors. 2019 Dec 18;12(1):591. doi: 10.1186/s13071-019-3850-8. Parasit Vectors. 2019. PMID: 31852489 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

