Outbreak of Salmonella Strathcona caused by datterino tomatoes, Denmark, 2011
- PMID: 26846608
- PMCID: PMC9150450
- DOI: 10.1017/S0950268816000121
Outbreak of Salmonella Strathcona caused by datterino tomatoes, Denmark, 2011
Abstract
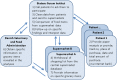
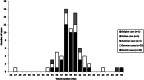
In September 2011, a patient cluster with a rare Salmonella serotype - Strathcona - was identified in Denmark. An outbreak investigation was initiated to reveal the source in order to stop the outbreak. In addition to hypothesis-generating interviews, comparable analyses of patients' household shopping receipts were conducted. A matched case-control study with 25 cases and 56 population register controls was conducted to test the findings of the hypothesis-generating investigation. In total, 43 cases of Salmonella Strathcona were reported in Denmark. Additionally, 28 cases were reported from Germany, Italy, Austria and Belgium. The results of the investigation in Denmark showed that 8/10 cases had bought datterino tomatoes prior to disease onset. Illness was associated with a specific supermarket chain [matched odds ratio (mOR) 16·9, 95% confidence interval (CI) 2·2-130], and having consumed elongated small tomatoes (OR 28·1, 95% CI 2·6-302). Traceback investigation showed that the tomatoes came from an Italian producer. This outbreak, linked to tomatoes, underpins the growing recognition of the broad source range of Salmonella and the ability of fresh produce to cause multi-country outbreaks. It is important to strengthen the international cooperation between public-health and food-safety authorities in the European Union to investigate future multi-country outbreaks in order to prevent illness from ready-to-eat produce.
Keywords: Case-control study; Salmonella; outbreaks.
Figures


Similar articles
-
2008 outbreak of Salmonella Saintpaul infections associated with raw produce.N Engl J Med. 2011 Mar 10;364(10):918-27. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1005741. Epub 2011 Feb 23. N Engl J Med. 2011. PMID: 21345092
-
Multistate outbreak of Salmonella serotype Typhimurium infections associated with consumption of restaurant tomatoes, USA, 2006: hypothesis generation through case exposures in multiple restaurant clusters.Epidemiol Infect. 2012 Nov;140(11):2053-61. doi: 10.1017/S0950268811002895. Epub 2012 Jan 20. Epidemiol Infect. 2012. PMID: 22261286
-
Outbreak of unusual H2S-negative monophasic Salmonella Typhimurium strain likely associated with small tomatoes, Sweden, August to October 2019.Euro Surveill. 2019 Nov;24(47):1900643. doi: 10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2019.24.47.1900643. Euro Surveill. 2019. PMID: 31771698 Free PMC article.
-
A prolonged outbreak of Salmonella Infantis associated with pork products in central Germany, April-October 2013.Epidemiol Infect. 2016 May;144(7):1429-39. doi: 10.1017/S0950268815002629. Epub 2015 Nov 23. Epidemiol Infect. 2016. PMID: 26593246 Free PMC article.
-
An outbreak of Salmonella Newport associated with mung bean sprouts in Germany and the Netherlands, October to November 2011.Euro Surveill. 2014 Jan 9;19(1):20665. doi: 10.2807/1560-7917.es2014.19.1.20665. Euro Surveill. 2014. PMID: 24434173
Cited by
-
Epidemiological, Genetic, and Phenotypic Characteristics of Non-Typhoidal Salmonella in Young Children, as Obtained from a Tertiary Hospital in Guangzhou, China.Microorganisms. 2023 Sep 28;11(10):2433. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms11102433. Microorganisms. 2023. PMID: 37894091 Free PMC article.
-
Colonization of Raphanus sativus by human pathogenic microorganisms.Front Microbiol. 2024 Feb 15;15:1296372. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1296372. eCollection 2024. Front Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38426059 Free PMC article.
-
Toward an Integrated Genome-Based Surveillance of Salmonella enterica in Germany.Front Microbiol. 2021 Feb 10;12:626941. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.626941. eCollection 2021. Front Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 33643254 Free PMC article.
-
A common framework for using and reporting consumer purchase data (CPD) in foodborne outbreak investigations in Europe.Infect Ecol Epidemiol. 2021 Dec 2;12(1):2007828. doi: 10.1080/20008686.2021.2007828. eCollection 2022. Infect Ecol Epidemiol. 2021. PMID: 34880966 Free PMC article.
-
Tomato Plant Microbiota under Conventional and Organic Fertilization Regimes in a Soilless Culture System.Microorganisms. 2023 Jun 22;11(7):1633. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms11071633. Microorganisms. 2023. PMID: 37512805 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Anon. Annual report on zoonoses in Denmark 2010. National Food Institute, Technical University of Denmark, 2011.
-
- Rabsch W, et al. The zoonotic agent Salmonella. In: Sing A, ed. Zoonoses – Infections Affecting Humans and Animals – Focus on Public Health Aspects. Dordrecht: Springer Science and Business Media, 2015, pp. 179–211.
-
- Hanning IB, Nutt JD, Ricke SC. Salmonellosis outbreaks in the United States due to fresh produce: sources and potential intervention measures. Foodborne Pathogens and Disease 2009; 6: 635–648. - PubMed
-
- Grimont PA, Weill FX. Antigenic Formulae of the Salmonella Serovars, 9th edn. Paris: Institut Pasteur, 2007.
-
- Ribot EM, et al. Standardization of pulsed field gel electrophoresis protocols for the subtyping of Escherichia coli O157:H7, Salmonella, and Shigella for PulseNet. Foodborne Pathogens and Disease 2006; 3: 59–67. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

