Arthralgias, fatigue, paresthesias and visceral pain: can joint hypermobility solve the puzzle? A case report
- PMID: 26846674
- PMCID: PMC4743317
- DOI: 10.1186/s12891-016-0905-2
Arthralgias, fatigue, paresthesias and visceral pain: can joint hypermobility solve the puzzle? A case report
Abstract
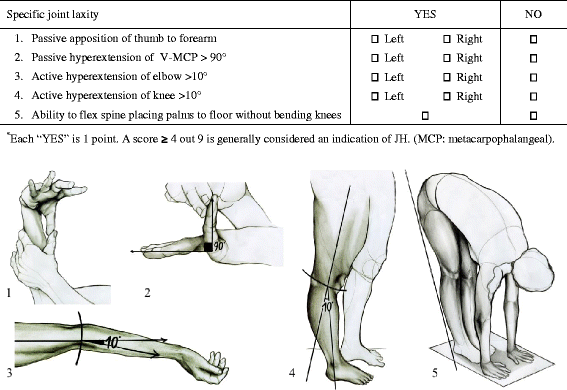
Background: Joint hypermobility syndrome describes a disorder in which musculoskeletal pain occurs in a generalized joint hypermobility substrate. The clinical picture comprises variable manifestations which involve mainly but not exclusively the musculoskeletal system, and evolve over the person's lifetime.
Case presentation: Describing the case of a 20-year-old female with generalized arthro-myalgias, persistent fatigue and troublesome visceral pain, we illustrate how a frequently ignored clinical sign such as joint hypermobility can be the keystone to clarify different simultaneous symptoms. All of the patient's physical complaints had been investigated separately during her previous medical examinations, and several tests repeatedly gave negative results. The patient received different diagnoses that describe only part of her problems, such as irritable bowel syndrome for visceral pain, fibromyalgia for arthralgias or depression for fatigue. These approaches gave rise to pharmacological or physical treatments which did not improve her quality of life in any way and in some instances worsened the situation. Pronounced joint hypermobility which led the patient to flex her joints excessively, causing subluxations in several districts, was the only sign overlooked.
Conclusion: Exploring the patient's articular features in her clinical context led us to diagnose joint hypermobility syndrome, a complex and often ignored condition. The case highlights the utility of a multidisciplinary approach and coordinated interventions to define and manage this clinical entity.
Similar articles
-
Joint hypermobility syndrome in childhood. A not so benign multisystem disorder?Rheumatology (Oxford). 2005 Jun;44(6):744-50. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/keh557. Epub 2005 Feb 22. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2005. PMID: 15728418
-
[Benign joint hypermobility syndrome--a case report: unrecognized or undiagnosed condition?].Reumatizam. 2010;57(1):48-52. Reumatizam. 2010. PMID: 20941940 Croatian.
-
Prevalence, injury rate and, symptom frequency in generalized joint laxity and joint hypermobility syndrome in a "healthy" college population.Clin Rheumatol. 2016 Apr;35(4):1029-39. doi: 10.1007/s10067-015-2951-9. Epub 2015 May 1. Clin Rheumatol. 2016. PMID: 25930211
-
Presentation of two cases with hypermobility syndrome and review of the related literature.Eur J Phys Rehabil Med. 2010 Mar;46(1):89-94. Eur J Phys Rehabil Med. 2010. PMID: 20332732 Review.
-
Neurodevelopmental attributes of joint hypermobility syndrome/Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, hypermobility type: Update and perspectives.Am J Med Genet C Semin Med Genet. 2015 Mar;169C(1):107-16. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.c.31424. Epub 2015 Feb 5. Am J Med Genet C Semin Med Genet. 2015. PMID: 25654988 Review.
Cited by
-
The Association Between Joint Laxity and Post-Dural Puncture Headache.Cureus. 2023 Jul 3;15(7):e41304. doi: 10.7759/cureus.41304. eCollection 2023 Jul. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 37539432 Free PMC article.
-
The biopsychosocial impact of hypermobility spectrum disorders in adults: a scoping review.Rheumatol Int. 2023 Jun;43(6):985-1014. doi: 10.1007/s00296-023-05298-2. Epub 2023 Mar 10. Rheumatol Int. 2023. PMID: 36894757 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Smith TO, Easton V, Bacon H, Jerman E, Armon K, Poland F, et al. The relationship between benign joint hypermobility syndrome and psychological distress: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Rheumatol (United Kingdom) 2014;53:114–122. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical