Tuning of the Na,K-ATPase by the beta subunit
- PMID: 26847162
- PMCID: PMC4742777
- DOI: 10.1038/srep20442
Tuning of the Na,K-ATPase by the beta subunit
Abstract
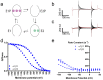
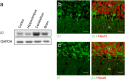
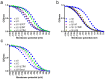
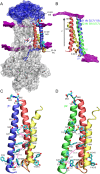
The vital gradients of Na(+) and K(+) across the plasma membrane of animal cells are maintained by the Na,K-ATPase, an αβ enzyme complex, whose α subunit carries out the ion transport and ATP hydrolysis. The specific roles of the β subunit isoforms are less clear, though β2 is essential for motor physiology in mammals. Here, we show that compared to β1 and β3, β2 stabilizes the Na(+)-occluded E1P state relative to the outward-open E2P state, and that the effect is mediated by its transmembrane domain. Molecular dynamics simulations further demonstrate that the tilt angle of the β transmembrane helix correlates with its functional effect, suggesting that the relative orientation of β modulates ion binding at the α subunit. β2 is primarily expressed in granule neurons and glomeruli in the cerebellum, and we propose that its unique functional characteristics are important to respond appropriately to the cerebellar Na(+) and K(+) gradients.
Figures
References
-
- Morth J. P. et al. Crystal structure of the sodium-potassium pump. Nature 450, 1043–1049 (2007). - PubMed
-
- Shinoda T., Ogawa H., Cornelius F. & Toyoshima C. Crytal Structure of the sodium-potassium pump at 2.4A resolution. Nature 459, 446–451 (2009). - PubMed
-
- Toyoshima C., Kanai R. & Cornelius F. First Crystal Structures of Na+,K+-ATPase: New Light on the Oldest Ion Pump. Structure 19, 1732–1738 (2011). - PubMed
-
- Kanai R., Ogawa H., Vilsen B., Cornelius F. & Toyoshima C. Crystal structure of a Na+-bound Na+,K+-ATPase preceding the E1P state. Nature 502, 201–6 (2013). - PubMed
-
- Nyblom M. et al. Crystal Structure of Na+, K+-ATPase in the Na+-Bound State. Science (80-.). 342, 123–127 (2013). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

