Validation of the Korean Version of the DN4 Diagnostic Questionnaire for Neuropathic Pain in Patients with Lumbar or Lumbar-Radicular Pain
- PMID: 26847299
- PMCID: PMC4740539
- DOI: 10.3349/ymj.2016.57.2.449
Validation of the Korean Version of the DN4 Diagnostic Questionnaire for Neuropathic Pain in Patients with Lumbar or Lumbar-Radicular Pain
Abstract
Purpose: To evaluate the diagnostic value of the Korean version of the Douleur Neuropathique 4 (DN4) questionnaire and to validate this questionnaire in terms of psychometric properties in patients with chronic pain due to degenerative spinal disease.
Materials and methods: The Korean version of the DN4 questionnaire, which was translated and linguistically validated by the MAPI Research Group, was tested on 83 patients with lumbar or lumbar-radicular pain. Test-retest reliability was evaluated in a subsample of 40 patients who completed two assessments with an interval of 2 weeks. Nociceptive pain and neuropathic component pain were diagnosed in 40 and 43 patients, respectively.
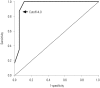
Results: The Cronbach's α coefficient of internal consistency was 0.819, and the test-retest intraclass correlation coefficient (3, 1) (95% confidence interval) was 0.813 (0.776-0.847) (n=40). The area under the receiver-operator characteristics curve was 0.953 (p<0.001), with 95% confidence interval between 0.869 and 0.990. The Korean version of the DN4 questionnaire showed a sensitivity of 100% and 87.1%, and a specificity of 88.2% and 94.1% at the cutoff value of 3/10 and 4/10, respectively, for discriminating neuropathic component pain.
Conclusion: The present study demonstrated the good discriminatory power of DN4 between nociceptive pain and neuropathic component pain in patients with lumbar or lumbar-radicular pain.
Keywords: Douleur Neuropathique 4 questionnaire; Korean language; Neuropathic pain; psychometric validation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no financial conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Reliability and validity of the Japanese translation of the DN4 Diagnostic Questionnaire in patients with neuropathic pain.J Anesth. 2018 Jun;32(3):403-408. doi: 10.1007/s00540-018-2495-7. Epub 2018 May 5. J Anesth. 2018. PMID: 29730769
-
Validation of a New Arabic Version of the Neuropathic Pain Diagnostic Questionnaire (DN4).Pain Pract. 2017 Jan;17(1):78-87. doi: 10.1111/papr.12419. Epub 2016 Feb 20. Pain Pract. 2017. PMID: 26895970
-
Validation of the Greek Version of the DN4 Diagnostic Questionnaire for Neuropathic Pain.Pain Pract. 2015 Sep;15(7):627-32. doi: 10.1111/papr.12221. Epub 2014 May 5. Pain Pract. 2015. PMID: 24796220
-
Joint European Academy of Neurology-European Pain Federation-Neuropathic Pain Special Interest Group of the International Association for the Study of Pain guidelines on neuropathic pain assessment.Eur J Neurol. 2023 Aug;30(8):2177-2196. doi: 10.1111/ene.15831. Epub 2023 May 30. Eur J Neurol. 2023. PMID: 37253688
-
The painDETECT project - far more than a screening tool on neuropathic pain.Curr Med Res Opin. 2016 Jun;32(6):1033-57. doi: 10.1185/03007995.2016.1157460. Epub 2016 Mar 11. Curr Med Res Opin. 2016. PMID: 26907456 Review.
Cited by
-
Neuropathic pain in Mali: The current situation, comprehensive hypothesis, which therapeutic strategy for Africa?eNeurologicalSci. 2021 Jan 9;22:100312. doi: 10.1016/j.ensci.2021.100312. eCollection 2021 Mar. eNeurologicalSci. 2021. PMID: 33537467 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Possible Neuropathic Pain in Clinical Practice-Review on Selected Diagnostic Tools and Its Further Challenges.Diagnostics (Basel). 2022 Dec 29;13(1):108. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics13010108. Diagnostics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36611400 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparison of treatment outcomes in lumbar central stenosis patients treated with epidural steroid injections: interlaminar versus bilateral transforaminal approach.Korean J Pain. 2020 Jul 1;33(3):226-233. doi: 10.3344/kjp.2020.33.3.226. Korean J Pain. 2020. PMID: 32606267 Free PMC article.
-
Reliability and validity of the Japanese translation of the DN4 Diagnostic Questionnaire in patients with neuropathic pain.J Anesth. 2018 Jun;32(3):403-408. doi: 10.1007/s00540-018-2495-7. Epub 2018 May 5. J Anesth. 2018. PMID: 29730769
-
Validation of Complete Hindi Version of Douleur Neuropathique 4 Questionnaire for Assessment of Neuropathic Pain.Indian J Palliat Care. 2021 Apr-Jun;27(2):257-263. doi: 10.25259/IJPC_340_20. Epub 2021 Aug 12. Indian J Palliat Care. 2021. PMID: 34511793 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sekiguchi M, Kikuchi S, Myers RR. Experimental spinal stenosis: relationship between degree of cauda equina compression, neuropathology, and pain. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2004;29:1105–1111. - PubMed
-
- Takahashi N, Arai I, Kayama S, Ichiji K, Fukuda H, Kaga T, et al. Therapeutic efficacy of pregabalin in patients with leg symptoms due to lumbar spinal stenosis. Fukushima J Med Sci. 2014;60:35–42. - PubMed
-
- Yaksi A, Ozgö;nenel L, Ozgönenel B. The efficiency of gabapentin therapy in patients with lumbar spinal stenosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2007;32:939–942. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

