Tuft cells, taste-chemosensory cells, orchestrate parasite type 2 immunity in the gut
- PMID: 26847546
- PMCID: PMC5528851
- DOI: 10.1126/science.aaf1648
Tuft cells, taste-chemosensory cells, orchestrate parasite type 2 immunity in the gut
Abstract
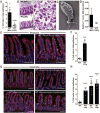
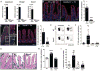
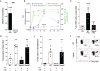
The intestinal epithelium forms an essential barrier between a host and its microbiota. Protozoa and helminths are members of the gut microbiota of mammals, including humans, yet the many ways that gut epithelial cells orchestrate responses to these eukaryotes remain unclear. Here we show that tuft cells, which are taste-chemosensory epithelial cells, accumulate during parasite colonization and infection. Disruption of chemosensory signaling through the loss of TRMP5 abrogates the expansion of tuft cells, goblet cells, eosinophils, and type 2 innate lymphoid cells during parasite colonization. Tuft cells are the primary source of the parasite-induced cytokine interleukin-25, which indirectly induces tuft cell expansion by promoting interleukin-13 production by innate lymphoid cells. Our results identify intestinal tuft cells as critical sentinels in the gut epithelium that promote type 2 immunity in response to intestinal parasites.
Copyright © 2016, American Association for the Advancement of Science.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures

Comment in
-
IMMUNOLOGY. The enigmatic tuft cell in immunity.Science. 2016 Mar 18;351(6279):1264-5. doi: 10.1126/science.aaf5215. Epub 2016 Mar 17. Science. 2016. PMID: 26989236 No abstract available.
-
Tuft Cells: A New Flavor in Innate Epithelial Immunity.Trends Parasitol. 2016 Aug;32(8):583-585. doi: 10.1016/j.pt.2016.04.016. Epub 2016 May 5. Trends Parasitol. 2016. PMID: 27161767
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

