Metformin inhibits growth of human non-small cell lung cancer cells via liver kinase B-1-independent activation of adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase
- PMID: 26847819
- PMCID: PMC4768996
- DOI: 10.3892/mmr.2016.4830
Metformin inhibits growth of human non-small cell lung cancer cells via liver kinase B-1-independent activation of adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase
Abstract
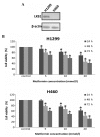
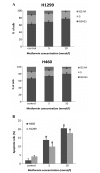
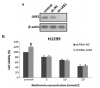
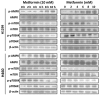
Metformin, the most widely administered oral anti‑diabetic therapeutic agent, exerts its glucose-lowering effect predominantly via liver kinase B1 (LKB1)-dependent activation of adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase (AMPK). Accumulating evidence has demonstrated that metformin possesses potential antitumor effects. However, whether the antitumor effect of metformin is via the LKB1/AMPK signaling pathway remains to be determined. In the current study, the effects of metformin on proliferation, cell cycle progression, and apoptosis of human non‑small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) H460 (LKB1‑null) and H1299 (LKB1‑positive) cells were assessed, and the role of LKB1/AMPK signaling in the anti‑growth effects of metformin were investigated. Cell viability was determined using a 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide assay, cell cycle distribution and apoptosis were assessed by flow cytometry, and protein expression levels were measured by western blotting. Metformin inhibited proliferation, induced significant cell cycle arrest at the G0‑G1 phase and increased apoptosis in NSCLC cells in a time- and concentration-dependent manner, regardless of the level of LKB1 protein expression. Furthermore, knockdown of LKB1 with short hairpin RNA (shRNA) did not affect the antiproliferative effect of metformin in the H1299 cells. Metformin stimulated AMPK phosphorylation and subsequently suppressed the phosphorylation of mammalian target of rapamycin and its downstream effector, 70‑kDa ribosomal protein S6 kinase in the two cell lines. These effects were abrogated by silencing AMPK with small interfering RNA (siRNA). In addition, knockdown of AMPK with siRNA inhibited the effect of metformin on cell proliferation in the two cell lines. These results provide evidence that the growth inhibition of metformin in NSCLC cells is mediated by LKB1‑independent activation of AMPK, indicating that metformin may be a potential therapeutic agent for the treatment of human NSCLC.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Metformin enhances cisplatin cytotoxicity by suppressing signal transducer and activator of transcription-3 activity independently of the liver kinase B1-AMP-activated protein kinase pathway.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2013 Aug;49(2):241-50. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2012-0244OC. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2013. PMID: 23526220
-
Synergistic effects of metformin treatment in combination with gefitinib, a selective EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor, in LKB1 wild-type NSCLC cell lines.Clin Cancer Res. 2013 Jul 1;19(13):3508-19. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-12-2777. Epub 2013 May 21. Clin Cancer Res. 2013. PMID: 23695170
-
Metformin amplifies chemotherapy-induced AMPK activation and antitumoral growth.Clin Cancer Res. 2011 Jun 15;17(12):3993-4005. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-10-2243. Epub 2011 May 4. Clin Cancer Res. 2011. PMID: 21543517
-
[Antitumor mechanism of metformin via adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase (AMPK) activation].Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2013 Aug 20;16(8):427-32. doi: 10.3779/j.issn.1009-3419.2013.08.07. Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2013. PMID: 23945247 Free PMC article. Review. Chinese.
-
Metformin and cancer.Rev Diabet Stud. 2013 Winter;10(4):228-35. doi: 10.1900/RDS.2013.10.228. Epub 2014 Feb 10. Rev Diabet Stud. 2013. PMID: 24841876 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Enhancing the anticancer potential of metformin: fabrication of efficient nanospanlastics, in vitro cytotoxic studies on HEP-2 cells and reactome enhanced pathway analysis.Int J Pharm X. 2023 Oct 23;6:100215. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpx.2023.100215. eCollection 2023 Dec 15. Int J Pharm X. 2023. PMID: 38024451 Free PMC article.
-
Metformin induces ZFP36 by mTORC1 inhibition in cervical cancer-derived cell lines.BMC Cancer. 2024 Jul 18;24(1):853. doi: 10.1186/s12885-024-12555-5. BMC Cancer. 2024. PMID: 39026155 Free PMC article.
-
Metformin therapy and the risk of colorectal adenoma in patients with type 2 diabetes: A meta-analysis.Oncotarget. 2017 Jan 31;8(5):8843-8853. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.13633. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 27903961 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Diabetes mellitus and survival of non-small cell lung cancer patients after surgery: A comprehensive systematic review and meta-analysis.Thorac Cancer. 2019 Mar;10(3):571-578. doi: 10.1111/1759-7714.12985. Epub 2019 Jan 31. Thorac Cancer. 2019. PMID: 30706684 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolic barriers in non-small cell lung cancer with LKB1 and/or KEAP1 mutations for immunotherapeutic strategies.Front Oncol. 2023 Aug 22;13:1249237. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1249237. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37675220 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Standards of medical care in diabetes - 2015: Summary of revisions. Diabetes Care. 2015;38(Suppl 4) No authors listed. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

