Physiological signalling to myosin phosphatase targeting subunit-1 phosphorylation in ileal smooth muscle
- PMID: 26847850
- PMCID: PMC4908025
- DOI: 10.1113/JP271703
Physiological signalling to myosin phosphatase targeting subunit-1 phosphorylation in ileal smooth muscle
Abstract
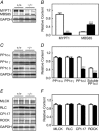
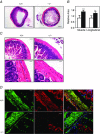
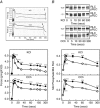
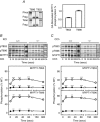
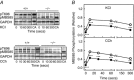
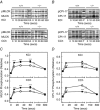
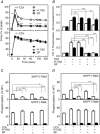
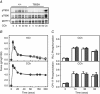
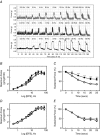
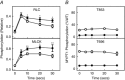
Key points: The extent of myosin regulatory light chain phosphorylation (RLC) necessary for smooth muscle contraction depends on the respective activities of Ca(2+) /calmodulin-dependent myosin light chain kinase and myosin light chain phosphatase (MLCP), which contains a regulatory subunit MYPT1 bound to the phosphatase catalytic subunit and myosin. MYPT1 showed significant constitutive T696 and T853 phosphorylation, which is predicted to inhibit MLCP activity in isolated ileal smooth muscle tissues, with additional phosphorylation upon pharmacological treatment with the muscarinic agonist carbachol. Electrical field stimulation (EFS), which releases ACh from nerves, increased force and RLC phosphorylation but not MYPT1 T696 or T853 phosphorylation. The conditional knockout of MYPT1 or the knockin mutation T853A in mice had no effect on the frequency-maximal force responses to EFS in isolated ileal tissues. Physiological RLC phosphorylation and force development in ileal smooth muscle depend on myosin light chain kinase and MLCP activities without changes in constitutive MYPT1 phosphorylation.
Abstract: Smooth muscle contraction initiated by myosin regulatory light chain (RLC) phosphorylation is dependent on the relative activities of Ca(2+) /calmodulin-dependent myosin light chain kinase (MLCK) and myosin light chain phosphatase (MLCP). We have investigated the physiological role of the MLCP regulatory subunit MYPT1 in ileal smooth muscle in adult mice with (1) smooth muscle-specific deletion of MYPT1; (2) non-phosphorylatable MYPT1 containing a T853A knockin mutation; and (3) measurements of force and protein phosphorylation responses to cholinergic neurostimulation initiated by electric field stimulation. Isolated MYPT1-deficient tissues from MYPT1(SM-/-) mice contracted and relaxed rapidly with moderate differences in sustained responses to KCl and carbachol treatments and washouts, respectively. Similarly, measurements of regulatory proteins responsible for RLC phosphorylation during contractions also revealed moderate changes. There were no differences in contractile or RLC phosphorylation responses to carbachol between tissues from normal mice vs. MYPT1 T853A knockin mice. Quantitatively, there was substantial MYPT1 T696 and T853 phosphorylation in wild-type tissues under resting conditions, predicting a high extent of MLCP phosphatase inhibition. Reduced PP1cδ activity in MYPT1-deficient tissues may be similar to attenuated MLCP activity in wild-type tissues resulting from constitutively phosphorylated MYPT1. Electric field stimulation increased RLC phosphorylation and force development in tissues from wild-type mice without an increase in MYPT1 phosphorylation. Thus, physiological RLC phosphorylation and force development in ileal smooth muscle appear to be dependent on MLCK and MLCP activities without changes in constitutive MYPT1 phosphorylation.
© 2016 The Authors. The Journal of Physiology © 2016 The Physiological Society.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Physiological vs. pharmacological signalling to myosin phosphorylation in airway smooth muscle.J Physiol. 2017 Oct 1;595(19):6231-6247. doi: 10.1113/JP274715. Epub 2017 Aug 24. J Physiol. 2017. PMID: 28749013 Free PMC article.
-
Constitutive phosphorylation of myosin phosphatase targeting subunit-1 in smooth muscle.J Physiol. 2014 Jul 15;592(14):3031-51. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2014.273011. Epub 2014 May 16. J Physiol. 2014. PMID: 24835173 Free PMC article.
-
In vivo roles for myosin phosphatase targeting subunit-1 phosphorylation sites T694 and T852 in bladder smooth muscle contraction.J Physiol. 2015 Feb 1;593(3):681-700. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2014.283853. Epub 2014 Dec 23. J Physiol. 2015. PMID: 25433069 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of Smooth Muscle Myosin Light Chain Phosphatase by Multisite Phosphorylation of the Myosin Targeting Subunit, MYPT1.Cardiovasc Hematol Disord Drug Targets. 2018;18(1):4-13. doi: 10.2174/1871529X18666180326120638. Cardiovasc Hematol Disord Drug Targets. 2018. PMID: 29577868 Review.
-
Protein kinase network in the regulation of phosphorylation and dephosphorylation of smooth muscle myosin light chain.Mol Cell Biochem. 2003 Jun;248(1-2):105-14. doi: 10.1023/a:1024180101032. Mol Cell Biochem. 2003. PMID: 12870661 Review.
Cited by
-
Genetic approaches to identify pathological limitations in aortic smooth muscle contraction.PLoS One. 2018 Mar 1;13(3):e0193769. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0193769. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 29494672 Free PMC article.
-
Diversity and plasticity in signaling pathways that regulate smooth muscle responsiveness: Paradigms and paradoxes for the myosin phosphatase, the master regulator of smooth muscle contraction.J Smooth Muscle Res. 2017;53(0):1-19. doi: 10.1540/jsmr.53.1. J Smooth Muscle Res. 2017. PMID: 28260704 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of myosin light chain phosphatase in cardiac physiology and pathophysiology.J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2016 Dec;101:35-43. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2016.10.004. Epub 2016 Oct 11. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2016. PMID: 27742556 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Excitatory cholinergic responses in mouse colon intramuscular interstitial cells of Cajal are due to enhanced Ca2+ release via M3 receptor activation.FASEB J. 2020 Aug;34(8):10073-10095. doi: 10.1096/fj.202000672R. Epub 2020 Jun 15. FASEB J. 2020. PMID: 32539213 Free PMC article.
-
Augmented contractility of murine femoral arteries in a streptozotocin diabetes model is related to increased phosphorylation of MYPT1.Physiol Rep. 2019 Feb;7(3):e13975. doi: 10.14814/phy2.13975. Physiol Rep. 2019. PMID: 30740930 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chen CP, Chen X, Qiao YN, Wang P, He WQ, Zhang CH, Zhao W, Gao YQ, Chen C, Tao T, Sun J, Wang Y, Gao N, Kamm KE, Stull JT & Zhu MS (2015). In vivo roles for myosin phosphatase targeting subunit‐1 phosphorylation sites T694 and T852 in bladder smooth muscle contraction. J Physiol 593, 681–700. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cole WC & Welsh DG (2011). Role of myosin light chain kinase and myosin light chain phosphatase in the resistance arterial myogenic response to intravascular pressure. Arch Biochem Biophys 510, 160–173. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

