Neuroprotective Effects Against POCD by Photobiomodulation: Evidence from Assembly/Disassembly of the Cytoskeleton
- PMID: 26848276
- PMCID: PMC4737522
- DOI: 10.4137/JEN.S33444
Neuroprotective Effects Against POCD by Photobiomodulation: Evidence from Assembly/Disassembly of the Cytoskeleton
Abstract
Postoperative cognitive dysfunction (POCD) is a decline in memory following anaesthesia and surgery in elderly patients. While often reversible, it consumes medical resources, compromises patient well-being, and possibly accelerates progression into Alzheimer's disease. Anesthetics have been implicated in POCD, as has neuroinflammation, as indicated by cytokine inflammatory markers. Photobiomodulation (PBM) is an effective treatment for a number of conditions, including inflammation. PBM also has a direct effect on microtubule disassembly in neurons with the formation of small, reversible varicosities, which cause neural blockade and alleviation of pain symptoms. This mimics endogenously formed varicosities that are neuroprotective against damage, toxins, and the formation of larger, destructive varicosities and focal swellings. It is proposed that PBM may be effective as a preconditioning treatment against POCD; similar to the PBM treatment, protective and abscopal effects that have been demonstrated in experimental models of macular degeneration, neurological, and cardiac conditions.
Keywords: PBM; POCD; cytoskeleton; neuroprotection; photobiomodulation; postoperative cognitive dysfunction.
Figures
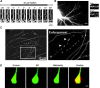
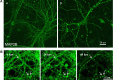
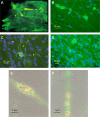
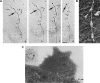
Similar articles
-
Paracetamol (acetaminophen) rescues cognitive decline, neuroinflammation and cytoskeletal alterations in a model of post-operative cognitive decline (POCD) in middle-aged rats.Sci Rep. 2021 May 12;11(1):10139. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-89629-y. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33980934 Free PMC article.
-
Current Progress on Neuroinflammation-mediated Postoperative Cognitive Dysfunction: An Update.Curr Mol Med. 2023;23(10):1077-1086. doi: 10.2174/1566524023666221118140523. Curr Mol Med. 2023. PMID: 36411553 Review.
-
Effects of prenatal photobiomodulation treatment on neonatal hypoxic ischemia in rat offspring.Theranostics. 2021 Jan 1;11(3):1269-1294. doi: 10.7150/thno.49672. eCollection 2021. Theranostics. 2021. PMID: 33391534 Free PMC article.
-
Auricular vagus nerve stimulation protects against postoperative cognitive dysfunction by attenuating neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration in aged rats.Neurosci Lett. 2019 Jun 11;703:104-110. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2019.03.034. Epub 2019 Mar 21. Neurosci Lett. 2019. PMID: 30904576
-
Photobiomodulation for the aging brain.Ageing Res Rev. 2021 Sep;70:101415. doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2021.101415. Epub 2021 Jul 26. Ageing Res Rev. 2021. PMID: 34325071 Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of conventional nursing in the operating room combined with transcutaneous electrical acupoint stimulation on postoperative cognitive dysfunction after total knee arthroplasty in elderly patients.J Orthop Surg Res. 2024 Feb 1;18(1):906. doi: 10.1186/s13018-023-04348-6. J Orthop Surg Res. 2024. PMID: 38297396 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Effect of bispectral index-guided anesthesia on consumption of anesthetics and early postoperative cognitive dysfunction after liver transplantation: An observational study.Medicine (Baltimore). 2017 Sep;96(35):e7966. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000007966. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017. PMID: 28858130 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanotransduction, cellular biophotonic activity, and signaling patterns for tissue regeneration.J Biol Chem. 2024 Nov;300(11):107847. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2024.107847. Epub 2024 Sep 30. J Biol Chem. 2024. PMID: 39357824 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dexmedetomidine attenuates the neuroinflammation and cognitive dysfunction in aged mice by targeting the SNHG14/miR‑340/NF‑κB axis.Biomed Rep. 2023 Oct 24;19(6):100. doi: 10.3892/br.2023.1682. eCollection 2023 Dec. Biomed Rep. 2023. PMID: 37954634 Free PMC article.
-
A Role for Photobiomodulation in the Prevention of Myocardial Ischemic Reperfusion Injury: A Systematic Review and Potential Molecular Mechanisms.Sci Rep. 2017 Feb 9;7:42386. doi: 10.1038/srep42386. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28181487 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hanning CD. Postoperative cognitive dysfunction. Br J Anaesth. 2005;95(1):82–87. - PubMed
-
- van Harten AE, Scheeren TWL, Absalom AR. A review of postoperative cognitive dysfunction and neuroinflammation associated with cardiac surgery and anaesthesia. Anaesthesia. 2012;67(3):280–293. - PubMed
-
- Fodale V, Santamaria LB, Schifilliti D, Mandal PK. Anaesthetics and postoperative cognitive dysfunction: a pathological mechanism mimicking Alzheimer’s disease. Anaesthesia. 2010;65(4):388–395. - PubMed
-
- Hamblin MR, Pires de Sousa MV, Arany PR, Carroll JD, Patthoff D. Low level laser (light) therapy and photobiomodulation: the path forward; Paper presented at: SPIE 9309, Mechanisms for Low-Light Therapy X; 2015.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

