Experimental measurement on movement of spiral-type capsule endoscope
- PMID: 26848279
- PMCID: PMC4723017
- DOI: 10.2147/MDER.S93168
Experimental measurement on movement of spiral-type capsule endoscope
Abstract
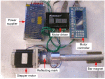
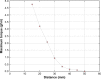
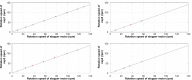
Wireless capsule endoscope achieved great success, however, the maneuvering of wireless capsule endoscope is challenging at present. A magnetic driving instrument, including two bar magnets, a stepper motor, a motor driver, a motor controller, and a power supplier, was developed to generate rotational magnetic fields. Permanent magnet ring, magnetized as S and N poles radially and mounted spiral structure on the surface, acted as a capsule. The maximum torque passing to the capsule, rotational synchronization of capsule and motor, and the translational speed of capsule, were measured in ex vivo porcine large intestine. The experimental results illustrate that the rotational movement of the spiral-type capsule in the intestine is feasible and the cost of the magnetic driving equipment is low. As a result, the solution is promising in the future controllability.
Keywords: magnet ring; magnetic driving; spiral structure; torque; wireless capsule endoscope.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Design and implementation of magnetically maneuverable capsule endoscope system with direction reference for image navigation.Proc Inst Mech Eng H. 2014 Jul;228(7):652-64. doi: 10.1177/0954411914540876. Epub 2014 Jul 22. Proc Inst Mech Eng H. 2014. PMID: 25052694
-
Closed Loop Control of a Tethered Magnetic Capsule Endoscope.Robot Sci Syst. 2016 Jun;2016:10.15607/RSS.2016.XII.018. doi: 10.15607/RSS.2016.XII.018. Robot Sci Syst. 2016. PMID: 28286886 Free PMC article.
-
A locomotion mechanism with external magnetic guidance for active capsule endoscope.Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2010;2010:4375-8. doi: 10.1109/IEMBS.2010.5627100. Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2010. PMID: 21096455
-
[Review of the active locomotion system for capsule endoscope].Sheng Wu Yi Xue Gong Cheng Xue Za Zhi. 2010 Feb;27(1):215-8. Sheng Wu Yi Xue Gong Cheng Xue Za Zhi. 2010. PMID: 20337057 Review. Chinese.
-
The optimization of wireless power transmission: design and realization.Int J Med Robot. 2012 Sep;8(3):337-47. doi: 10.1002/rcs.1428. Epub 2012 Apr 17. Int J Med Robot. 2012. PMID: 22508580 Review.
References
-
- Iddan G, Meron G, Glukhovsky A, Swain P. Wireless capsule endoscopy. Nature. 2000;405:417. - PubMed
-
- Meng MQ-H, Mei T, Pu J, Hu C, Wang X, Chan Y. Wireless robotic capsule endoscopy: state-of-the-art and challenges; Proceedings of the 5th World Congress on Intelligent Control and Automation; June 15–19 2004; Hangzhou, People’s Republic of China.
-
- Moglia A, Menciassi A, Dario P, Cuschieri A. Capsule endoscopy: progress update and challenges ahead. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2009;6:353–361. - PubMed
-
- Rasouli M, Kencana AP, Van An Huynh, Kiat Ting E, Lai JCY, Phee LSJ. Wireless capsule endoscopes for enhanced diagnostic inspection of gastrointestinal tract; 2010 IEEE Conference on Robotics Automation and Mechatronics; June 28–30 2010; Singapore.
-
- Waghmare PV, Panchal CV, Poul BN. Swallowable wireless capsular endoscopy: a novel breakthrough in the biomedical industry and future progress. Int J Pharm Sci Res. 2013;4:4133–4144.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

