Relationship between HMGB1 and PAI-1 after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation
- PMID: 26848281
- PMCID: PMC4723029
- DOI: 10.2147/JBM.S93008
Relationship between HMGB1 and PAI-1 after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation
Abstract
Background: Conditioning regimens including total body irradiation (TBI) or cyclophosphamide can mobilize high-mobility group box 1 (HMGB1) to peripheral blood. Additionally, increased plasminogen activator inhibitor (PAI)-1 levels are associated with post-allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (aHSCT). However, changes to circulating levels of HMGB1 after aHSCT are poorly understood.
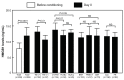
Materials and methods: The study cohort included 289 patients who underwent aHSCT at one of 25 institutions in Japan. We have investigated the relationship between HMGB1 and PAI-1 following aHSCT. A significant increase in HMGB1 levels occurred after conditioning treatment. Additionally, levels of HMGB1 at day 0 were significantly increased in TBI+ patients and cyclophosphamide/TBI patients.
Conclusion: Our data revealed that an increased level of HMGB1 at day 0 following aHSCT correlates with increased PAI-1 after aHSCT, which is consistent with previous reports. Increased HMGB1 at day 0 after a conditioning regimen may play a role in transplantation-associated coagulopathy following aHSCT, because PAI-1 can accelerate procoagulant activity.
Keywords: HMGB1; PAI-1; TBI; aHSCT; transplantation-associated coagulopathy.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Metabolic Potential of the Gut Microbiome Is Significantly Impacted by Conditioning Regimen in Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation Recipients.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Sep 21;23(19):11115. doi: 10.3390/ijms231911115. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36232416 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of total body irradiation plus cyclophosphamide with busulfan plus cyclophosphamide as conditioning regimens in patients with acute lymphoblastic leukemia undergoing allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplant.Leuk Lymphoma. 2013 Nov;54(11):2474-9. doi: 10.3109/10428194.2013.779691. Epub 2013 Mar 27. Leuk Lymphoma. 2013. PMID: 23442062
-
Comparison of conditioning regimens for autologous stem cell transplantation in children with acute myeloid leukemia: A nationwide retrospective study in Japan.Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2019 Jan;66(1):e27459. doi: 10.1002/pbc.27459. Epub 2018 Sep 30. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2019. PMID: 30270523
-
Maximizing the benefit of allogeneic stem cell transplantation in myelodysplastic syndromes.Semin Hematol. 2017 Jul;54(3):154-158. doi: 10.1053/j.seminhematol.2017.06.002. Epub 2017 Jun 21. Semin Hematol. 2017. PMID: 28958289 Review.
-
Allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation for multiple myeloma.Biomed Pharmacother. 2002 May;56(3):133-8. doi: 10.1016/s0753-3322(02)00175-0. Biomed Pharmacother. 2002. PMID: 12046684 Review.
Cited by
-
Biomarkers of graft-vs-host disease: Understanding and applications for the future.World J Transplant. 2021 Aug 18;11(8):335-343. doi: 10.5500/wjt.v11.i8.335. World J Transplant. 2021. PMID: 34447670 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Danger Signals and Graft-versus-host Disease: Current Understanding and Future Perspectives.Front Immunol. 2016 Nov 29;7:539. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2016.00539. eCollection 2016. Front Immunol. 2016. PMID: 27965667 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prioritization of genes involved in endothelial cell apoptosis by their implication in lymphedema using an analysis of associative gene networks with ANDSystem.BMC Med Genomics. 2019 Mar 13;12(Suppl 2):47. doi: 10.1186/s12920-019-0492-9. BMC Med Genomics. 2019. PMID: 30871556 Free PMC article.
-
Potentially life-threatening coagulopathy associated with simultaneous reduction in coagulation and fibrinolytic function in pediatric acute leukemia after hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation.Int J Hematol. 2017 Jul;106(1):126-134. doi: 10.1007/s12185-017-2213-5. Epub 2017 Mar 16. Int J Hematol. 2017. PMID: 28303518
-
High mobility group box 1 (HMGB1): a pivotal regulator of hematopoietic malignancies.J Hematol Oncol. 2020 Jul 13;13(1):91. doi: 10.1186/s13045-020-00920-3. J Hematol Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32660524 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Cantoni N, Gerull S, Heim D, et al. Order of application and liver toxicity in patients given BU and CY containing conditioning regimens for allogeneic hematopoietic SCT. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2011;46:344–349. - PubMed
-
- Kuniyasu A, Tokunaga M, Yamamoto T, et al. Oxidized LDL and lysophosphatidylcholine stimulate plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 expression through reactive oxygen species generation and ERK1/2 activation in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2011;1811:153–162. - PubMed
-
- Salat C, Holler E, Kolb HJ, et al. Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 confirms diagnosis of hepatic veno-occlusive disease in patients with hyperbilirubinemia after bone marrow transplantation. Blood. 1997;89:2184–2188. - PubMed
-
- Pihusch M, Wegner H, Goehring P, et al. Diagnosis of hepatic veno-occlusive disease by plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 plasma antigen levels: a prospective analysis in 350 allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell recipients. Transplantation. 2005;80:1376–1382. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

