Minimizing eddy currents induced in the ground plane of a large phased-array ultrasound applicator for echo-planar imaging-based MR thermometry
- PMID: 26848391
- PMCID: PMC4741031
- DOI: 10.1186/s40349-016-0047-x
Minimizing eddy currents induced in the ground plane of a large phased-array ultrasound applicator for echo-planar imaging-based MR thermometry
Abstract
Background: The study aims to investigate different ground plane segmentation designs of an ultrasound transducer to reduce gradient field induced eddy currents and the associated geometric distortion and temperature map errors in echo-planar imaging (EPI)-based MR thermometry in transcranial magnetic resonance (MR)-guided focused ultrasound (tcMRgFUS).
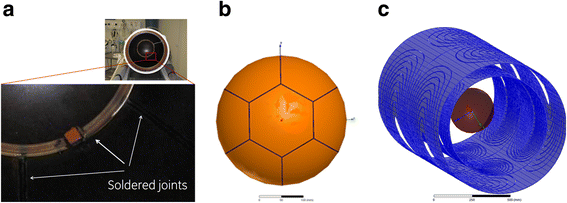
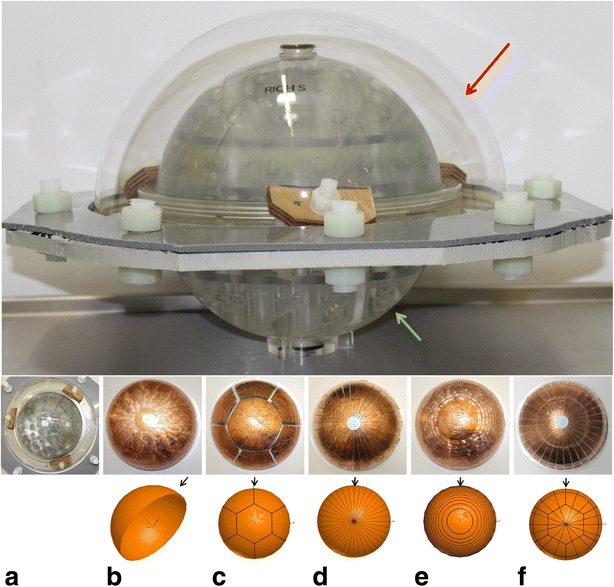
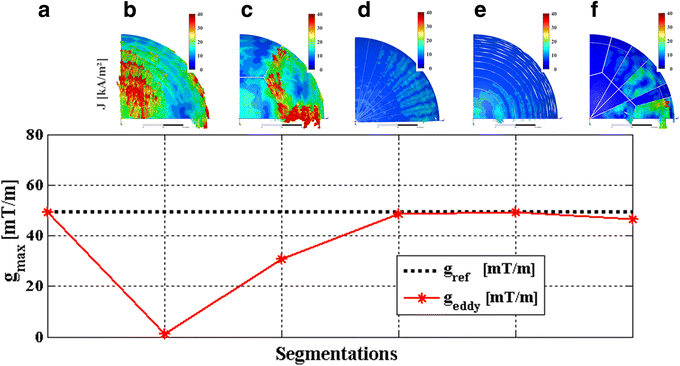
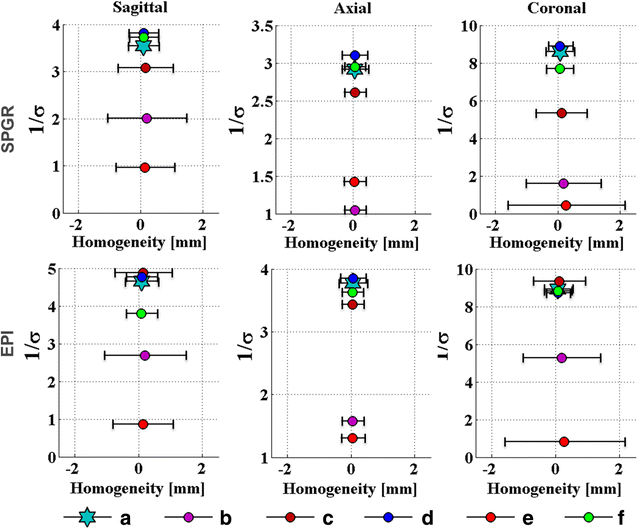
Methods: Six different ground plane segmentations were considered and the efficacy of each in suppressing eddy currents was investigated in silico and in operando. For the latter case, the segmented ground planes were implemented in a transducer mockup model for validation. Robust spoiled gradient (SPGR) echo sequences and multi-shot EPI sequences were acquired. For each sequence and pattern, geometric distortions were quantified in the magnitude images and expressed in millimeters. Phase images were used for extracting the temperature maps on the basis of the temperature-dependent proton resonance frequency shift phenomenon. The means, standard deviations, and signal-to-noise ratios (SNRs) were extracted and contrasted with the geometric distortions of all patterns.
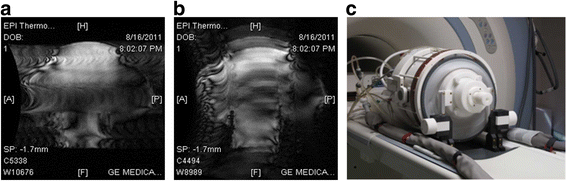
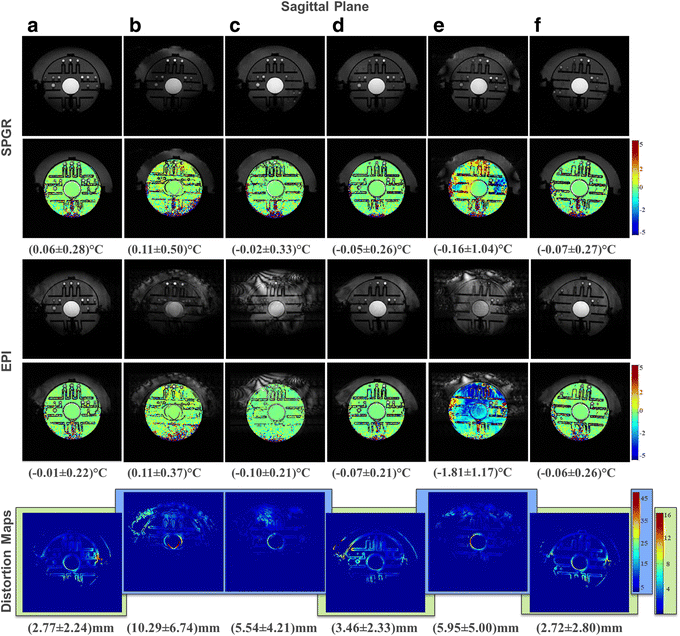
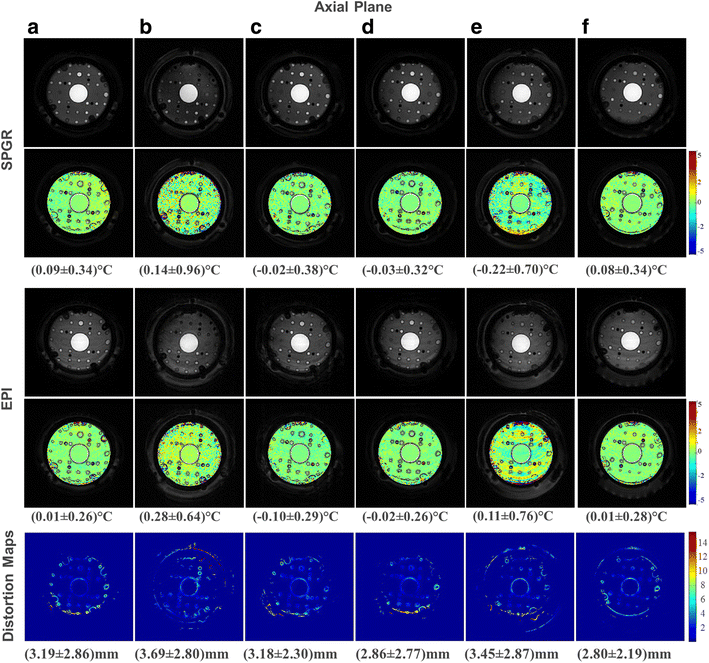
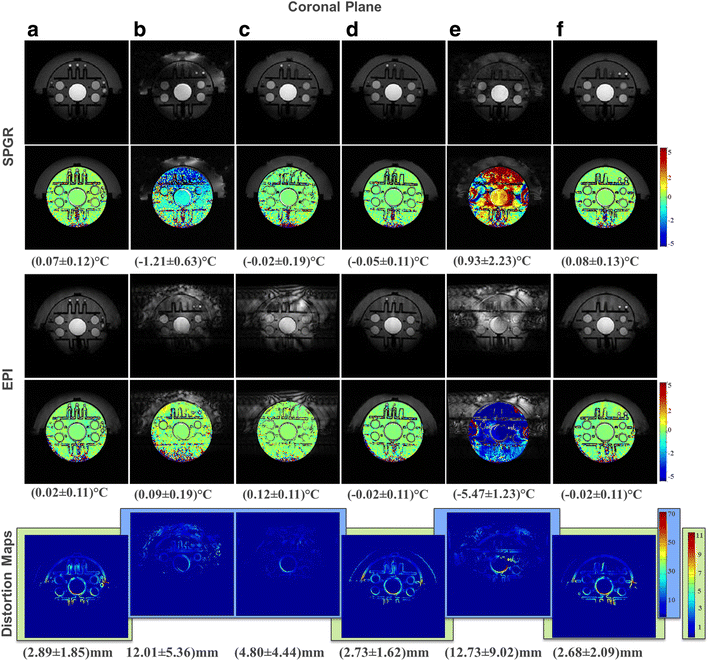
Results: The geometric distortion analysis and temperature map evaluations showed that more than one pattern could be considered the best-performing transducer. In the sagittal plane, the star (d) (3.46 ± 2.33 mm) and star-ring patterns (f) (2.72 ± 2.8 mm) showed smaller geometric distortions than the currently available seven-segment sheet (c) (5.54 ± 4.21 mm) and were both comparable to the reference scenario (a) (2.77 ± 2.24 mm). Contrasting these results with the temperature maps revealed that (d) performs as well as (a) in SPGR and EPI.
Conclusions: We demonstrated that segmenting the transducer ground plane into a star pattern reduces eddy currents to a level wherein multi-plane EPI for accurate MR thermometry in tcMRgFUS is feasible.
Keywords: Echo-planar imaging; Eddy currents; Focused ultrasound; MR thermometry; Phased-array transducer; Proton resonance frequency shift.
Figures
References
-
- Hindman JC. Proton resonance shift of water in gas and liquid states. Journal of Chemical Physics. 1966;44:4582–4592. doi: 10.1063/1.1726676. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

