Dramatic Response of a Large, 10 Cm Hepatocellular Carcinoma to Monotherapy with Yttrium-90 Based Selective Internal Radiation Therapy
- PMID: 26848414
- PMCID: PMC4727862
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.425
Dramatic Response of a Large, 10 Cm Hepatocellular Carcinoma to Monotherapy with Yttrium-90 Based Selective Internal Radiation Therapy
Abstract
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is predominantly diagnosed in advanced stages and not amenable to surgical resection and transplantation. Systemic therapies have had a limited efficacy in treating HCC. Although HCC is a radiosensitive tumor, treatments with external-beam radiation are limited by radiosensitivity of normal liver tissue and surrounding organs-at-risk, i.e. bowel, stomach, and kidney. Several large retrospective series have demonstrated a modest effect of selective internal radiation therapy (SIRT) with Yttrium-90 ((90)Y) microspheres in unresectable HCC, both in terms of tumor response and survival. The authors present a patient with an extremely large, multifocal, unresectable HCC who achieved a dramatic response with SIRT treatment.
Keywords: hepatocellular carcinoma; radioactive embolization; sirt; tumor embolization.
Conflict of interest statement
One of the authors, Dr. Fred Moeslein, is a proctor for Sirtex. He has no other affiliations with Sirtex and no other financial ties.
Figures
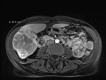
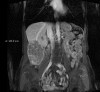
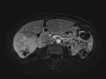
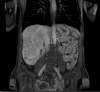
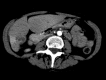
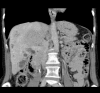
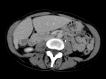
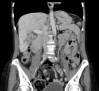
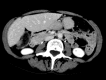
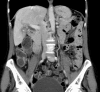
Similar articles
-
Treatment options for unresectable HCC with a focus on SIRT with Yttrium-90 resin microspheres.Int J Clin Pract. 2017 Nov;71(11). doi: 10.1111/ijcp.12972. Epub 2017 Jul 30. Int J Clin Pract. 2017. PMID: 28758319 Review.
-
Conformal external beam radiation or selective internal radiation therapy-a comparison of treatment outcomes for hepatocellular carcinoma.J Gastrointest Oncol. 2016 Jun;7(3):433-40. doi: 10.21037/jgo.2015.10.04. J Gastrointest Oncol. 2016. PMID: 27284477 Free PMC article.
-
Single administration of Selective Internal Radiation Therapy versus continuous treatment with sorafeNIB in locally advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (SIRveNIB): study protocol for a phase iii randomized controlled trial.BMC Cancer. 2016 Nov 7;16(1):856. doi: 10.1186/s12885-016-2868-y. BMC Cancer. 2016. PMID: 27821083 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Comparison of the survival and tolerability of radioembolization in elderly vs. younger patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma.J Hepatol. 2013 Oct;59(4):753-61. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2013.05.025. Epub 2013 May 23. J Hepatol. 2013. PMID: 23707371 Clinical Trial.
-
Treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma by radioembolization using 90Y microspheres.Dig Dis. 2009;27(2):164-9. doi: 10.1159/000218349. Epub 2009 Jun 22. Dig Dis. 2009. PMID: 19546555 Review.
References
-
- Response to radioembolization with yttrium-90 resin microspheres may allow surgical treatment with curative intent and prolonged survival in previously unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. Iñarrairaegui M, Pardo F, Bilbao JI, Rotellar F, Benito A, D'Avola D, Herrero JI, Rodriguez M, Martí P, Zozaya G, Dominguez I, Quiroga J, Sangro B. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2012;38:594–601. - PubMed
-
- Radioembolization with yttrium-90 glass microspheres in hepatocellular carcinoma: European experience on safety and long-term survival. Hilgard P, Hamami M, Fouly AE, Scherag A, Müller S, Ertle J, Heusner T, Cicinnati VR, Paul A, Bockisch A, Gerken G, Antoch G. Hepatology. 2010;52:1741–1749. - PubMed
-
- Selective internal radiation therapy for nonresectable hepatocellular carcinoma with intraarterial infusion of 90yttrium microspheres. Lau WY, Ho S, Leung TW, Chan M, Ho R, Johnson PJ, Li AK. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1998;40:583–592. - PubMed
-
- What determines survival duration in hepatocellular carcinoma treated with intraarterial Yttrium-90 microspheres? Lau WY, Ho S, Leung WT, Chan M, Lee WY, Johnson PJ. Hepatogastroenterology. 2001;48:338–340. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
