Presurgical Mapping of the Language Network Using Resting-state Functional Connectivity
- PMID: 26848557
- PMCID: PMC4833007
- DOI: 10.1097/RMR.0000000000000073
Presurgical Mapping of the Language Network Using Resting-state Functional Connectivity
Abstract
Resting-state functional magnetic resonance imaging (resting-state fMRI) is a tool for investigating the functional networks that arise during the resting state of the brain. Recent advances of the resting-state fMRI analysis suggest its feasibility for evaluating language function. The most common clinical application is for presurgical mapping of cortex for a brain tumor or for resective epilespy surgery. In this article, we review the techniques and presurgical applications of resting-state fMRI analysis for language evaluation, and discuss the use in the clinical setting, focusing on planning for neurosurgery.
Figures
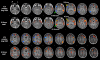
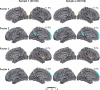

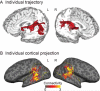
Similar articles
-
Language Mapping Using fMRI and Direct Cortical Stimulation for Brain Tumor Surgery: The Good, the Bad, and the Questionable.Top Magn Reson Imaging. 2016 Feb;25(1):1-10. doi: 10.1097/RMR.0000000000000074. Top Magn Reson Imaging. 2016. PMID: 26848555 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Resting-state functional MRI in pediatric epilepsy surgery.Pediatr Neurosurg. 2013;49(5):261-73. doi: 10.1159/000363605. Epub 2014 Sep 24. Pediatr Neurosurg. 2013. PMID: 25277135 Review.
-
Real-time presurgical resting-state fMRI in patients with brain tumors: Quality control and comparison with task-fMRI and intraoperative mapping.Hum Brain Mapp. 2020 Feb 15;41(3):797-814. doi: 10.1002/hbm.24840. Epub 2019 Nov 6. Hum Brain Mapp. 2020. PMID: 31692177 Free PMC article.
-
Presurgical brain mapping of the language network in pediatric patients with epilepsy using resting-state fMRI.J Neurosurg Pediatr. 2021 Jan 8;27(3):259-268. doi: 10.3171/2020.8.PEDS20517. Print 2021 Mar 1. J Neurosurg Pediatr. 2021. PMID: 33418528
-
Clinical Resting-state fMRI in the Preoperative Setting: Are We Ready for Prime Time?Top Magn Reson Imaging. 2016 Feb;25(1):11-8. doi: 10.1097/RMR.0000000000000075. Top Magn Reson Imaging. 2016. PMID: 26848556 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Role of Functional Imaging Techniques to Assess Motor and Language Cortical Plasticity in Glioma Patients: A Systematic Review.Neural Plast. 2019 Nov 11;2019:4056436. doi: 10.1155/2019/4056436. eCollection 2019. Neural Plast. 2019. PMID: 31814822 Free PMC article.
-
Language processing in Internet use disorder: Task-based fMRI study.PLoS One. 2022 Jun 24;17(6):e0269979. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0269979. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 35749379 Free PMC article.
-
Functional MRI for Surgery of Gliomas.Curr Treat Options Neurol. 2017 Aug 23;19(10):34. doi: 10.1007/s11940-017-0469-y. Curr Treat Options Neurol. 2017. PMID: 28831723 Review.
-
Mapping language function with task-based vs. resting-state functional MRI.PLoS One. 2020 Jul 31;15(7):e0236423. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0236423. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32735611 Free PMC article.
-
Determination of Differences in Seed-Based Resting State Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging Language Networks in Pediatric Patients with Left- and Right-Lateralized Language: A Pilot Study.J Epilepsy Res. 2019 Dec 31;9(2):93-102. doi: 10.14581/jer.19011. eCollection 2019 Dec. J Epilepsy Res. 2019. PMID: 32509544 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dion JE, Gates PC, Fox AJ, et al. Clinical events following neuroangiography: a prospective study. Stroke. 1987;18:997–1004. - PubMed
-
- Snyder PJ, Harris LJ. The intracarotid amobarbital procedure: an historical perspective. Brain Cogn. 1997;33:18–32. - PubMed
-
- De Paola L, Mader MJ, Germiniani FM, et al. Bizarre behavior during intracarotid sodium amytal testing (WADA test): are they predictable? Arq Neuropsiquiatr. 2004;62:444–8. - PubMed
-
- Dym RJ, Burns J, Freeman K, et al. Is functional MR imaging assessment of hemispheric language dominance as good as the Wada test?: a meta-analysis. Radiology. 2011;261:446–55. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

