Presurgical Mapping of the Language Network Using Resting-state Functional Connectivity
- PMID: 26848557
- PMCID: PMC4833007
- DOI: 10.1097/RMR.0000000000000073
Presurgical Mapping of the Language Network Using Resting-state Functional Connectivity
Abstract
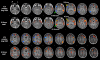
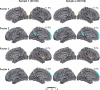
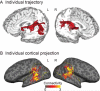
Resting-state functional magnetic resonance imaging (resting-state fMRI) is a tool for investigating the functional networks that arise during the resting state of the brain. Recent advances of the resting-state fMRI analysis suggest its feasibility for evaluating language function. The most common clinical application is for presurgical mapping of cortex for a brain tumor or for resective epilespy surgery. In this article, we review the techniques and presurgical applications of resting-state fMRI analysis for language evaluation, and discuss the use in the clinical setting, focusing on planning for neurosurgery.
Figures

References
-
- Dion JE, Gates PC, Fox AJ, et al. Clinical events following neuroangiography: a prospective study. Stroke. 1987;18:997–1004. - PubMed
-
- Snyder PJ, Harris LJ. The intracarotid amobarbital procedure: an historical perspective. Brain Cogn. 1997;33:18–32. - PubMed
-
- De Paola L, Mader MJ, Germiniani FM, et al. Bizarre behavior during intracarotid sodium amytal testing (WADA test): are they predictable? Arq Neuropsiquiatr. 2004;62:444–8. - PubMed
-
- Dym RJ, Burns J, Freeman K, et al. Is functional MR imaging assessment of hemispheric language dominance as good as the Wada test?: a meta-analysis. Radiology. 2011;261:446–55. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

