eIF4B is a convergent target and critical effector of oncogenic Pim and PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathways in Abl transformants
- PMID: 26848623
- PMCID: PMC4891105
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.7164
eIF4B is a convergent target and critical effector of oncogenic Pim and PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathways in Abl transformants
Abstract
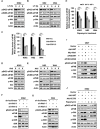
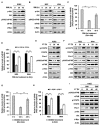
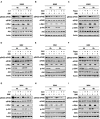
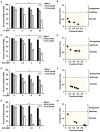
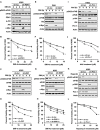
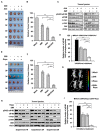
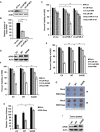
Activation of eIF4B correlates with Abl-mediated cellular transformation, but the precise mechanisms are largely unknown. Here we show that eIF4B is a convergent substrate of JAK/STAT/Pim and PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathways in Abl transformants. Both pathways phosphorylated eIF4B in Abl-transformed cells, and such redundant regulation was responsible for the limited effect of single inhibitor on Abl oncogenicity. Persistent inhibition of one signaling pathway induced the activation of the other pathway and thereby restored the phosphorylation levels of eIF4B. Simultaneous inhibition of the two pathways impaired eIF4B phosphorylation more effectively, and synergistically induced apoptosis in Abl transformed cells and inhibited the growth of engrafted tumors in nude mice. Similarly, the survival of Abl transformants exhibited a higher sensitivity to the pharmacological inhibition, when combined with the shRNA-based silence of the other pathway. Interestingly, such synergy was dependent on the phosphorylation status of eIF4B on Ser422, as overexpression of eIF4B phosphomimetic mutant S422E in the transformants greatly attenuated the synergistic effects of these inhibitors on Abl oncogenicity. In contrast, eIF4B knockdown sensitized Abl transformants to undergo apoptosis induced by the combined blockage. Collectively, the results indicate that eIF4B integrates the signals from Pim and PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathways in Abl-expressing leukemic cells, and is a promising therapeutic target for such cancers.
Keywords: AKT; Abl oncogene; Pim kinase; eIF4B; tumorigenesis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Chen J-L, Limnander A, Rothman PB. Pim-1 and Pim-2 kinases are required for efficient pre–B-cell transformation by v-Abl oncogene. Blood. 2008;111:1677–1685. - PubMed
-
- Marega M, Piazza RG, Pirola A, Redaelli S, Mogavero A, Iacobucci I, Meneghetti I, Parma M, Pogliani EM, Gambacorti-Passerini C. BCR and BCR-ABL regulation during myeloid differentiation in healthy donors and in chronic phase/blast crisis CML patients. Leukemia. 2010;24:1445–1449. - PubMed
-
- Pecquet C, Nyga R, Penard-Lacronique V, Smithgall TE, Murakami H, Regnier A, Lassoued K, Gouilleux F. The Src tyrosine kinase Hck is required for Tel-Abl- but not for Tel-Jak2-induced cell transformation. Oncogene. 2006;26:1577–1585. - PubMed
-
- Yang J, Wang J, Chen K, Guo G, Xi R, Rothman PB, Whitten D, Zhang L, Huang S, Chen J-L. eIF4B Phosphorylation by Pim Kinases Plays a Critical Role in Cellular Transformation by Abl Oncogenes. Cancer Research. 2013;73:4898–4908. - PubMed
-
- Guo G, Qiu X, Wang S, Chen Y, Rothman PB, Wang Z, Chen Y, Wang G, Chen JL. Oncogenic E17K mutation in the pleckstrin homology domain of AKT1 promotes v-Abl-mediated pre-B-cell transformation and survival of Pim-deficient cells. Oncogene. 2010;29:3845–3853. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

