CD93 and dystroglycan cooperation in human endothelial cell adhesion and migration adhesion and migration
- PMID: 26848865
- PMCID: PMC4891106
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.7136
CD93 and dystroglycan cooperation in human endothelial cell adhesion and migration adhesion and migration
Abstract
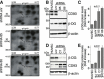
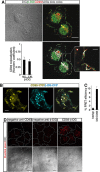
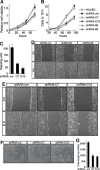
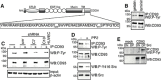
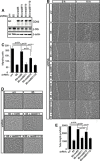
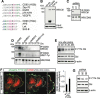
CD93 is a transmembrane glycoprotein predominantly expressed in endothelial cells. Although CD93 displays proangiogenic activity, its molecular function in angiogenesis still needs to be clarified. To get molecular insight into the biological role of CD93 in the endothelium, we performed proteomic analyses to examine changes in the protein profile of endothelial cells after CD93 silencing. Among differentially expressed proteins, we identified dystroglycan, a laminin-binding protein involved in angiogenesis, whose expression is increased in vascular endothelial cells within malignant tumors. Using immunofluorescence, FRET, and proximity ligation analyses, we observed a close interaction between CD93 and β-dystroglycan. Moreover, silencing experiments showed that CD93 and dystroglycan promoted endothelial cell migration and organization into capillary-like structures. CD93 proved to be phosphorylated on tyrosine 628 and 644 following cell adhesion on laminin through dystroglycan. This phosphorylation was shown to be necessary for a proper endothelial migratory phenotype. Moreover, we showed that during cell spreading phosphorylated CD93 recruited the signaling protein Cbl, which in turn was phosphorylated on tyrosine 774. Altogether, our results identify a new signaling pathway which is activated by the cooperation between CD93 and dystroglycan and involved in the control of endothelial cell function.
Keywords: C1qRp; Cbl; Src; angiogenesis; signal transduction.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Lamalice L, Le Boeuf F, Huot J. Endothelial cell migration during angiogenesis. Circ Res. 2007;100:782–794. - PubMed
-
- Carmeliet P. Angiogenesis in health and disease. Nat Med. 2003;9:653–660. - PubMed
-
- Greenlee MC, Sullivan SA, Bohlson SS. CD93 and related family members: their role in innate immunity. Curr Drug Targets. 2008;9:130–138. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

