Network Analysis of a Comprehensive Knowledge Repository Reveals a Dual Role for Ceramide in Alzheimer's Disease
- PMID: 26849355
- PMCID: PMC4752297
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0148431
Network Analysis of a Comprehensive Knowledge Repository Reveals a Dual Role for Ceramide in Alzheimer's Disease
Abstract
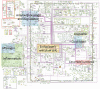
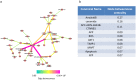
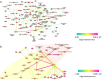
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is the most common cause of senile dementia. Many inflammatory factors such as amyloid-β and pro-inflammatory cytokines are known to contribute to the inflammatory response in the AD brain. Sphingolipids are widely known to have roles in the pathogenesis of inflammatory diseases, where the precise roles for sphingolipids in inflammation-associated pathogenesis of AD are not well understood. Here we performed a network analysis to clarify the importance of sphingolipids and to model relationships among inflammatory factors and sphingolipids in AD. In this study, we have updated sphingolipid signaling and metabolic cascades in a map of AD signaling networks that we named "AlzPathway," a comprehensive knowledge repository of signaling pathways in AD. Our network analysis of the updated AlzPathway indicates that the pathways related to ceramide are one of the primary pathways and that ceramide is one of the important players in the pathogenesis of AD. The results of our analysis suggest the following two prospects about inflammation in AD: (1) ceramide could play important roles in both inflammatory and anti-inflammatory pathways of AD, and (2) several factors such as Sphingomyelinase and Siglec-11 may be associated with ceramide related inflammation and anti-inflammation pathways in AD. In this study, network analysis of comprehensive knowledge repository reveals a dual role for ceramide in AD. This result provides a clue to clarify sphingolipids related inflammatory and anti-inflammatory pathways in AD.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Pathological roles of ceramide and its metabolites in metabolic syndrome and Alzheimer's disease.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014 May;1841(5):793-8. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2013.08.002. Epub 2013 Aug 13. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014. PMID: 23948264 Review.
-
AlzPathway, an Updated Map of Curated Signaling Pathways: Towards Deciphering Alzheimer's Disease Pathogenesis.Methods Mol Biol. 2016;1303:423-32. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-2627-5_25. Methods Mol Biol. 2016. PMID: 26235082
-
Ganglioside and related-sphingolipid profiles are altered in a cellular model of Alzheimer's disease.Biochimie. 2017 Jun;137:158-164. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2017.03.019. Epub 2017 Mar 29. Biochimie. 2017. PMID: 28365364
-
Ceramide/Sphingosine 1-Phosphate Axis as a Key Target for Diagnosis and Treatment in Alzheimer's Disease and Other Neurodegenerative Diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jul 22;23(15):8082. doi: 10.3390/ijms23158082. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35897658 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ceramide Metabolism Balance, a Multifaceted Factor in Critical Steps of Breast Cancer Development.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Aug 26;19(9):2527. doi: 10.3390/ijms19092527. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30149660 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Systematic druggable genome-wide Mendelian randomisation identifies therapeutic targets for Alzheimer's disease.J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2023 Nov;94(11):954-961. doi: 10.1136/jnnp-2023-331142. Epub 2023 Jun 22. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2023. PMID: 37349091 Free PMC article.
-
The relationship among amyloid-β deposition, sphingomyelin level, and the expression and function of P-glycoprotein in Alzheimer's disease pathological process.Neural Regen Res. 2023 Jun;18(6):1300-1307. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.358607. Neural Regen Res. 2023. PMID: 36453415 Free PMC article.
-
Orosomucoid Proteins Interact with the Small Subunit of Serine Palmitoyltransferase and Contribute to Sphingolipid Homeostasis and Stress Responses in Arabidopsis.Plant Cell. 2016 Dec;28(12):3038-3051. doi: 10.1105/tpc.16.00574. Epub 2016 Dec 6. Plant Cell. 2016. PMID: 27923879 Free PMC article.
-
Network Theoretical Approach to Explore Factors Affecting Signal Propagation and Stability in Dementia's Protein-Protein Interaction Network.Biomolecules. 2022 Mar 15;12(3):451. doi: 10.3390/biom12030451. Biomolecules. 2022. PMID: 35327643 Free PMC article.
-
Harnessing the paradoxical phenotypes of APOE ɛ2 and APOE ɛ4 to identify genetic modifiers in Alzheimer's disease.Alzheimers Dement. 2021 May;17(5):831-846. doi: 10.1002/alz.12240. Epub 2020 Dec 7. Alzheimers Dement. 2021. PMID: 33576571 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

