Changes in Soluble CD18 in Murine Autoimmune Arthritis and Rheumatoid Arthritis Reflect Disease Establishment and Treatment Response
- PMID: 26849368
- PMCID: PMC4743942
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0148486
Changes in Soluble CD18 in Murine Autoimmune Arthritis and Rheumatoid Arthritis Reflect Disease Establishment and Treatment Response
Abstract
Introduction: In rheumatoid arthritis (RA) immune activation and presence of autoantibodies may precede clinical onset of disease, and joint destruction can progress despite remission. However, the underlying temporal changes of such immune system abnormalities in the inflammatory response during treat-to-target strategies remain poorly understood. We have previously reported low levels of the soluble form of CD18 (sCD18) in plasma from patients with chronic RA and spondyloarthritis. Here, we study the changes of sCD18 before and during treatment of early RA and following arthritis induction in murine models of rheumatoid arthritis.
Methods: The level of sCD18 was analyzed with a time-resolved immunoflourometric assay in 1) plasma from early treatment naïve RA patients during a treat-to-target strategy (the OPERA cohort), 2) plasma from chronic RA patients, 3) serum from SKG and CIA mice following arthritis induction, and 4) supernatants from synovial fluid mononuclear cells (SFMCs) and peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) from 6 RA patients cultured with TNFα or adalimumab.
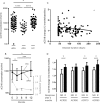
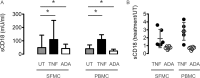
Results: Plasma levels of sCD18 were decreased in chronic RA patients compared with early RA patients and in early RA patients compared with healthy controls. After 12 months of treatment the levels in early RA patients were similar to healthy controls. This normalization of plasma sCD18 levels was more pronounced in patients with very early disease who achieved an early ACR response. Plasma sCD18 levels were associated with radiographic progression. Correspondingly, the serum level of sCD18 was decreased in SKG mice 6 weeks after arthritis induction compared with healthy littermates. The sCD18 levels in both SKG and CIA mice exhibited a biphasic course after arthritis induction with an initial increase above baseline followed by a decline. Shedding of CD18 from RA SFMC and RA PBMC cultures was increased by TNFα and decreased by adalimumab.
Conclusions: The plasma sCD18 levels were altered in patients with RA, in mice with autoimmune arthritis and in cell cultures treated with TNFα and adalimumab. Decreased levels of plasma sCD18 could reflect autoimmunity in transition from early to chronic disease and normalization in response to treatment could reflect autoimmunity in remission.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Decreased plasma levels of soluble CD18 link leukocyte infiltration with disease activity in spondyloarthritis.Arthritis Res Ther. 2014 Feb 4;16(1):R42. doi: 10.1186/ar4471. Arthritis Res Ther. 2014. PMID: 24490631 Free PMC article.
-
The interleukin-20 receptor axis in early rheumatoid arthritis: novel links between disease-associated autoantibodies and radiographic progression.Arthritis Res Ther. 2016 Mar 11;18:61. doi: 10.1186/s13075-016-0964-7. Arthritis Res Ther. 2016. PMID: 26968800 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Soluble OX40L is associated with presence of autoantibodies in early rheumatoid arthritis.Arthritis Res Ther. 2014 Oct 30;16(5):474. doi: 10.1186/s13075-014-0474-4. Arthritis Res Ther. 2014. PMID: 25359291 Free PMC article.
-
Structural joint damage and hand bone loss in patients with rheumatoid arthritis.Dan Med J. 2018 Mar;65(3):B5452. Dan Med J. 2018. PMID: 29510810 Review.
-
Remission, a therapeutic goal in inflammatory arthropathies? Clinical data from adalimumab studies.Drugs. 2006;66(14):1783-95. doi: 10.2165/00003495-200666140-00001. Drugs. 2006. PMID: 17040110 Review.
Cited by
-
Rheumatoid arthritis mediator CD18 expression by Staphylococcus aureus superantigen C in rats.Iran J Microbiol. 2019 Aug;11(4):337-344. Iran J Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31719966 Free PMC article.
-
Large soluble CD18 complexes with exclusive ICAM-1-binding properties are shed during immune cell migration in inflammation.J Transl Autoimmun. 2025 Jan 5;10:100266. doi: 10.1016/j.jtauto.2025.100266. eCollection 2025 Jun. J Transl Autoimmun. 2025. PMID: 39867459 Free PMC article.
-
Structural Immunology of Complement Receptors 3 and 4.Front Immunol. 2018 Nov 26;9:2716. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.02716. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30534123 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of β2 Integrins on Osteoclasts, Macrophages, Chondrocytes, and Synovial Fibroblasts in Osteoarthritis.Biomolecules. 2022 Nov 8;12(11):1653. doi: 10.3390/biom12111653. Biomolecules. 2022. PMID: 36359003 Free PMC article. Review.
-
IL-12/IL-23p40 identified as a downstream target of apremilast in ex vivo models of arthritis.Ther Adv Musculoskelet Dis. 2019 Feb 22;11:1759720X19828669. doi: 10.1177/1759720X19828669. eCollection 2019. Ther Adv Musculoskelet Dis. 2019. PMID: 30833991 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Springer TA. Adhesion receptors of the immune system. Nature. 1990;346: 425–434. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

