GRK2 Up-Regulation Creates a Positive Feedback Loop for Catecholamine Production in Chromaffin Cells
- PMID: 26849467
- PMCID: PMC5414648
- DOI: 10.1210/me.2015-1305
GRK2 Up-Regulation Creates a Positive Feedback Loop for Catecholamine Production in Chromaffin Cells
Abstract
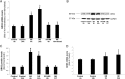
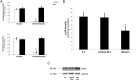
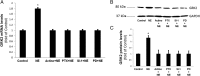
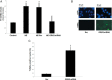
Elevated sympathetic nervous system (SNS) activity aggravates several diseases, including heart failure. The molecular cause(s) underlying this SNS hyperactivity are not known. We have previously uncovered a neurohormonal mechanism, operating in adrenomedullary chromaffin cells, by which circulating catecholamine (CA) levels increase in heart failure: severe dysfunction of the adrenal α2-adrenergic receptors (ARs) due to the up-regulation of G protein-coupled receptor-kinase (GRK)-2, the kinase that desensitizes them. Herein we looked at the potential signaling mechanisms that bring about this GRK2 elevation in chromaffin cells. We found that chronic CA treatment of either PC12 or rat primary chromaffin cells can in itself result in GRK2 transcriptional up-regulation through α2ARs-Gi/o proteins-Src-ERK1/2. The resultant GRK2 increase severely enhances the α2AR desensitization/down-regulation elevating not only CA release but also CA biosynthesis, as evidenced by tyrosine hydroxylase up-regulation. Finally, GRK2 knockdown leads to enhanced apoptosis of PC12 cells, indicating an essential role for GRK2 in chromaffin cell homeostasis/survival. In conclusion, chromaffin cell GRK2 mediates a positive feedback loop that feeds into CA secretion, thereby enabling the adrenomedullary component of the SNS to turn itself on.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Differential Modulation of Catecholamine and Adipokine Secretion by the Short Chain Fatty Acid Receptor FFAR3 and α2-Adrenergic Receptors in PC12 Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 May 11;25(10):5227. doi: 10.3390/ijms25105227. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38791266 Free PMC article.
-
Blockade of β-adrenoceptors restores the GRK2-mediated adrenal α(2) -adrenoceptor-catecholamine production axis in heart failure.Br J Pharmacol. 2012 Aug;166(8):2430-40. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2012.01972.x. Br J Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 22519418 Free PMC article.
-
Reduction of sympathetic activity via adrenal-targeted GRK2 gene deletion attenuates heart failure progression and improves cardiac function after myocardial infarction.J Biol Chem. 2010 May 21;285(21):16378-86. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.077859. Epub 2010 Mar 29. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20351116 Free PMC article.
-
Alpha2-adrenoceptors in adrenomedullary chromaffin cells: functional role and pathophysiological implications.Pflugers Arch. 2018 Jan;470(1):61-66. doi: 10.1007/s00424-017-2059-y. Epub 2017 Aug 23. Pflugers Arch. 2018. PMID: 28836008 Review.
-
GPCRs of adrenal chromaffin cells & catecholamines: The plot thickens.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2016 Aug;77(Pt B):213-9. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2016.02.003. Epub 2016 Feb 3. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2016. PMID: 26851510 Review.
Cited by
-
Impact of Aldosterone on the Failing Myocardium: Insights from Mitochondria and Adrenergic Receptors Signaling and Function.Cells. 2021 Jun 19;10(6):1552. doi: 10.3390/cells10061552. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34205363 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RGS proteins and cardiovascular Angiotensin II Signaling: Novel opportunities for therapeutic targeting.Biochem Pharmacol. 2023 Dec;218:115904. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2023.115904. Epub 2023 Nov 3. Biochem Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37922976 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Deletion of Osteopontin Enhances β₂-Adrenergic Receptor-Dependent Anti-Fibrotic Signaling in Cardiomyocytes.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Mar 20;20(6):1396. doi: 10.3390/ijms20061396. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 30897705 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting GPCR-Gβγ-GRK2 signaling as a novel strategy for treating cardiorenal pathologies.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2017 Aug;1863(8):1883-1892. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2017.01.020. Epub 2017 Jan 25. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2017. PMID: 28130200 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cyclic Adenosine Monophosphate in Cardiac and Sympathoadrenal GLP-1 Receptor Signaling: Focus on Anti-Inflammatory Effects.Pharmaceutics. 2024 May 22;16(6):693. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16060693. Pharmaceutics. 2024. PMID: 38931817 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

