The Unfolded Protein Response Plays a Predominant Homeostatic Role in Response to Mitochondrial Stress in Pancreatic Stellate Cells
- PMID: 26849807
- PMCID: PMC4743835
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0148999
The Unfolded Protein Response Plays a Predominant Homeostatic Role in Response to Mitochondrial Stress in Pancreatic Stellate Cells
Abstract
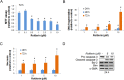
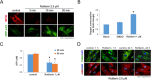
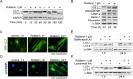
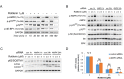
Activated pancreatic stellate cells (PaSC) are key participants in the stroma of pancreatic cancer, secreting extracellular matrix proteins and inflammatory mediators. Tumors are poorly vascularized, creating metabolic stress conditions in cancer and stromal cells that necessitate adaptive homeostatic cellular programs. Activation of autophagy and the endoplasmic reticulum unfolded protein response (UPR) have been described in hepatic stellate cells, but the role of these processes in PaSC responses to metabolic stress is unknown. We reported that the PI3K/mTOR pathway, which AMPK can regulate through multiple inputs, modulates PaSC activation and fibrogenic potential. Here, using primary and immortalized mouse PaSC, we assess the relative contributions of AMPK/mTOR signaling, autophagy and the UPR to cell fate responses during metabolic stress induced by mitochondrial dysfunction. The mitochondrial uncoupler rottlerin at low doses (0.5-2.5 μM) was added to cells cultured in 10% FBS complete media. Mitochondria rapidly depolarized, followed by altered mitochondrial dynamics and decreased cellular ATP levels. This mitochondrial dysfunction elicited rapid, sustained AMPK activation, mTOR pathway inhibition, and blockade of autophagic flux. Rottlerin treatment also induced rapid, sustained PERK/CHOP UPR signaling. Subsequently, high doses (>5 μM) induced loss of cell viability and cell death. Interestingly, AMPK knock-down using siRNA did not prevent rottlerin-induced mTOR inhibition, autophagy, or CHOP upregulation, suggesting that AMPK is dispensable for these responses. Moreover, CHOP genetic deletion, but not AMPK knock-down, prevented rottlerin-induced apoptosis and supported cell survival, suggesting that UPR signaling is a major modulator of cell fate in PaSC during metabolic stress. Further, short-term rottlerin treatment reduced both PaSC fibrogenic potential and IL-6 mRNA expression. In contrast, expression levels of the angiogenic factors HGF and VEGFα were unaffected, and the immune modulator IL-4 was markedly upregulated. These data imply that metabolic stress-induced PaSC reprogramming differentially modulates neighboring cells in the tumor microenvironment.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
CGK733-induced LC3 II formation is positively associated with the expression of cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p21Waf1/Cip1 through modulation of the AMPK and PERK/CHOP signaling pathways.Oncotarget. 2015 Nov 24;6(37):39692-701. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.5625. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 26486079 Free PMC article.
-
α-Solanine induces ROS-mediated autophagy through activation of endoplasmic reticulum stress and inhibition of Akt/mTOR pathway.Cell Death Dis. 2015 Aug 27;6(8):e1860. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2015.219. Cell Death Dis. 2015. PMID: 26313911 Free PMC article.
-
Curcumin induces apoptotic cell death of activated human CD4+ T cells via increasing endoplasmic reticulum stress and mitochondrial dysfunction.Int Immunopharmacol. 2013 Mar;15(3):517-23. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2013.02.002. Epub 2013 Feb 15. Int Immunopharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23415873
-
Unfolding anti-tumor immunity: ER stress responses sculpt tolerogenic myeloid cells in cancer.J Immunother Cancer. 2017 Jan 17;5:5. doi: 10.1186/s40425-016-0203-4. eCollection 2017. J Immunother Cancer. 2017. PMID: 28105371 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tripping on TRIB3 at the junction of health, metabolic dysfunction and cancer.Biochimie. 2016 May;124:34-52. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2016.02.005. Epub 2016 Feb 6. Biochimie. 2016. PMID: 26855171 Review.
Cited by
-
RB1CC1-enhanced autophagy facilitates PSCs activation and pancreatic fibrogenesis in chronic pancreatitis.Cell Death Dis. 2018 Sep 20;9(10):952. doi: 10.1038/s41419-018-0980-4. Cell Death Dis. 2018. PMID: 30237496 Free PMC article.
-
Human Pancreatic Acinar Cells: Proteomic Characterization, Physiologic Responses, and Organellar Disorders in ex Vivo Pancreatitis.Am J Pathol. 2017 Dec;187(12):2726-2743. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2017.08.017. Epub 2017 Sep 19. Am J Pathol. 2017. PMID: 28935577 Free PMC article.
-
Spatial profiling of endoplasmic reticulum stress markers in tumor associated cells predicts patient outcomes in pancreatic cancer.Neoplasia. 2025 Feb;60:101115. doi: 10.1016/j.neo.2024.101115. Epub 2025 Jan 15. Neoplasia. 2025. PMID: 39818177 Free PMC article.
-
Kinin B1R Activation Induces Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress in Primary Hypothalamic Neurons.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Mar 8;13:841068. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.841068. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35350763 Free PMC article.
-
Aqueous Extract of Descuraniae Semen Attenuates Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Inflammation and Apoptosis by Regulating the Proteasomal Degradation and IRE1α-Dependent Unfolded Protein Response in A549 Cells.Front Immunol. 2022 Jun 24;13:916102. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.916102. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35812413 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bachem MG, Schneider E, Gross H, Weidenbach H, Schmid RM, Menke A, et al. Identification, culture, and characterization of pancreatic stellate cells in rats and humans. Gastroenterology. 1998;115(2):421–32. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

