The Replisome-Coupled E3 Ubiquitin Ligase Rtt101Mms22 Counteracts Mrc1 Function to Tolerate Genotoxic Stress
- PMID: 26849847
- PMCID: PMC4743919
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1005843
The Replisome-Coupled E3 Ubiquitin Ligase Rtt101Mms22 Counteracts Mrc1 Function to Tolerate Genotoxic Stress
Abstract
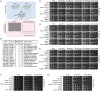
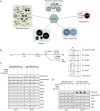
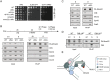
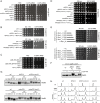
Faithful DNA replication and repair requires the activity of cullin 4-based E3 ubiquitin ligases (CRL4), but the underlying mechanisms remain poorly understood. The budding yeast Cul4 homologue, Rtt101, in complex with the linker Mms1 and the putative substrate adaptor Mms22 promotes progression of replication forks through damaged DNA. Here we characterized the interactome of Mms22 and found that the Rtt101(Mms22) ligase associates with the replisome progression complex during S-phase via the amino-terminal WD40 domain of Ctf4. Moreover, genetic screening for suppressors of the genotoxic sensitivity of rtt101Δ cells identified a cluster of replication proteins, among them a component of the fork protection complex, Mrc1. In contrast to rtt101Δ and mms22Δ cells, mrc1Δ rtt101Δ and mrc1Δ mms22Δ double mutants complete DNA replication upon replication stress by facilitating the repair/restart of stalled replication forks using a Rad52-dependent mechanism. Our results suggest that the Rtt101(Mms22) E3 ligase does not induce Mrc1 degradation, but specifically counteracts Mrc1's replicative function, possibly by modulating its interaction with the CMG (Cdc45-MCM-GINS) complex at stalled forks.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Mms1 and Mms22 stabilize the replisome during replication stress.Mol Biol Cell. 2011 Jul 1;22(13):2396-408. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E10-10-0848. Epub 2011 May 18. Mol Biol Cell. 2011. PMID: 21593207 Free PMC article.
-
Replisome function during replicative stress is modulated by histone h3 lysine 56 acetylation through Ctf4.Genetics. 2015 Apr;199(4):1047-63. doi: 10.1534/genetics.114.173856. Epub 2015 Feb 18. Genetics. 2015. PMID: 25697176 Free PMC article.
-
Rtt101 and Mms1 in budding yeast form a CUL4(DDB1)-like ubiquitin ligase that promotes replication through damaged DNA.EMBO Rep. 2008 Oct;9(10):1034-40. doi: 10.1038/embor.2008.155. Epub 2008 Aug 15. EMBO Rep. 2008. PMID: 18704118 Free PMC article.
-
Prevention of unwanted recombination at damaged replication forks.Curr Genet. 2020 Dec;66(6):1045-1051. doi: 10.1007/s00294-020-01095-7. Epub 2020 Jul 15. Curr Genet. 2020. PMID: 32671464 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Eukaryotic CMG Helicase at the Replication Fork: Emerging Architecture Reveals an Unexpected Mechanism.Bioessays. 2018 Mar;40(3):10.1002/bies.201700208. doi: 10.1002/bies.201700208. Epub 2018 Feb 6. Bioessays. 2018. PMID: 29405332 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Discovery and characterization of potent And-1 inhibitors for cancer treatment.Clin Transl Med. 2021 Dec;11(12):e627. doi: 10.1002/ctm2.627. Clin Transl Med. 2021. PMID: 34923765 Free PMC article.
-
Rtt101-Mms1-Mms22 coordinates replication-coupled sister chromatid cohesion and nucleosome assembly.EMBO Rep. 2017 Aug;18(8):1294-1305. doi: 10.15252/embr.201643807. Epub 2017 Jun 14. EMBO Rep. 2017. PMID: 28615292 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of Replication Fork Advance and Stability by Nucleosome Assembly.Genes (Basel). 2017 Jan 24;8(2):49. doi: 10.3390/genes8020049. Genes (Basel). 2017. PMID: 28125036 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Rfa1-MN-based system reveals new factors involved in the rescue of broken replication forks.PLoS Genet. 2025 Apr 1;21(4):e1011405. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1011405. eCollection 2025 Apr. PLoS Genet. 2025. PMID: 40168399 Free PMC article.
-
Yeast Genome Maintenance by the Multifunctional PIF1 DNA Helicase Family.Genes (Basel). 2020 Feb 20;11(2):224. doi: 10.3390/genes11020224. Genes (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32093266 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

