Divergent adherence estimates with pharmacokinetic and behavioural measures in the MTN-003 (VOICE) study
- PMID: 26850270
- PMCID: PMC4744323
- DOI: 10.7448/IAS.19.1.20642
Divergent adherence estimates with pharmacokinetic and behavioural measures in the MTN-003 (VOICE) study
Abstract
Introduction: In the Microbicide Trial Network MTN-003 (VOICE) study, a Phase IIB pre-exposure prophylaxis trial of daily oral or vaginal tenofovir (TFV), product adherence was poor based on pharmacokinetic (PK) drug detection in a random subsample. Here, we sought to compare behavioural and PK measures of adherence and examined correlates of adherence misreporting.
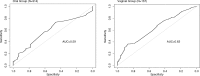
Methods: We included participants with PK and behavioural data from VOICE random subsample. Behavioural assessments included face-to-face interviews (FTFI), audio computer-assisted self-interviewing (ACASI) and pharmacy-returned product counts (PC). TFV concentrations < 0.31 ng/mL in plasma (oral group) and < 8.5 ng/swab in vaginal group were defined as "PK non-adherent." Logistic regression models were fit to calculate the combined predictive ability of the behavioural measures as summarized by area under the curve (AUC). Baseline characteristics associated with over-reporting daily product use relative to PK measures was assessed using a Generalized Linear Mixed Model.
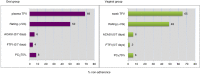
Results: In this random adherence cohort of VOICE participants assigned to active products, (N = 472), PK non-adherence was 69% in the oral group (N = 314) and 65% in the vaginal group (N = 158). Behaviourally, ≤ 10% of the cohort reported low/none use with any behavioural measure and accuracy was low (≤ 43%). None of the regression models had an AUC > 0.65 for any single or combined behavioural measures. Significant (p < 0.05) correlates of over-reporting included being very worried about getting HIV and being unmarried for the oral group; whereas for the vaginal group, being somewhat worried about HIV was associated with lower risk of over-reporting.
Conclusions: PK measures indicated similarly low adherence for the oral and vaginal groups. No behavioural measure accurately predicted PK non-adherence. Accurate real-time measures to monitor product adherence are urgently needed.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT00705679.
Keywords: HIV; adherence measurement; microbicide; pharmacokinetic drug detection; pre-exposure prophylaxis.
Figures

References
-
- FDA approves first drug for reducing the risk of sexually acquired HIV infection. U.S. Food and Drug Administration [Internet] 2012. [cited 8 Jan 2015]. Available from: http://www.fda.gov/NewsEvents/Newsroom/PressAnnouncements/ucm312210.htm.
-
- Thigpen MC, Kebaabetswe PM, Paxton LA, Smith DK, Rose CE, Segolodi TM, et al. Antiretroviral preexposure prophylaxis for heterosexual HIV transmission in Botswana. N Engl J Med. 2012;367(5):423–34. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

