The MBOAT7-TMC4 Variant rs641738 Increases Risk of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Individuals of European Descent
- PMID: 26850495
- PMCID: PMC4844071
- DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2016.01.032
The MBOAT7-TMC4 Variant rs641738 Increases Risk of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Individuals of European Descent
Abstract
Background & aims: Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is a leading cause of liver damage and is characterized by steatosis. Genetic factors increase risk for progressive NAFLD. A genome-wide association study showed that the rs641738 C>T variant in the locus that contains the membrane bound O-acyltransferase domain-containing 7 gene (MBOAT7, also called LPIAT1) and transmembrane channel-like 4 gene (TMC4) increased the risk for cirrhosis in alcohol abusers. We investigated whether the MBOAT7-TMC4 is a susceptibility locus for the development and progression of NAFLD.
Methods: We genotyped rs641738 in DNA collected from 3854 participants from the Dallas Heart Study (a multi-ethnic population-based probability sample of Dallas County residents) and 1149 European individuals from the Liver Biopsy Cross-Sectional Cohort. Clinical and anthropometric data were collected, and biochemical and lipidomics were measured in plasma samples from participants. A total of 2736 participants from the Dallas Heart Study also underwent proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy to measure hepatic triglyceride content. In the Liver Biopsy Cross-Sectional Cohort, a total of 1149 individuals underwent liver biopsy to diagnose liver disease and disease severity.
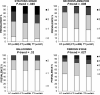
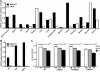
Results: The genotype rs641738 at the MBOAT7-TMC4 locus associated with increased hepatic fat content in the 2 cohorts, and with more severe liver damage and increased risk of fibrosis compared with subjects without the variant. MBOAT7, but not TMC4, was found to be highly expressed in the liver. The MBOAT7 rs641738 T allele was associated with lower protein expression in the liver and changes in plasma phosphatidylinositol species consistent with decreased MBOAT7 function.
Conclusions: We provide evidence for an association between the MBOAT7 rs641738 variant and the development and severity of NAFLD in individuals of European descent. This association seems to be mediated by changes in the hepatic phosphatidylinositol acyl-chain remodeling.
Keywords: Arachidonic Acid; NASH; PNPLA3; TM6SF2.
Copyright © 2016 AGA Institute. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Kleiner DE, Brunt EM, Van Natta M, et al. Design and validation of a histological scoring system for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology. 2005;41:1313–21. - PubMed
-
- Day CP. From fat to inflammation. Gastroenterology. 2006;130:207–10. - PubMed
-
- Bugianesi E, Leone N, Vanni E, et al. Expanding the natural history of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: from cryptogenic cirrhosis to hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology. 2002;123:134–40. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

