Cellular and molecular insight into the inhibition of primary root growth of Arabidopsis induced by peptaibols, a class of linear peptide antibiotics mainly produced by Trichoderma spp
- PMID: 26850879
- PMCID: PMC4809282
- DOI: 10.1093/jxb/erw023
Cellular and molecular insight into the inhibition of primary root growth of Arabidopsis induced by peptaibols, a class of linear peptide antibiotics mainly produced by Trichoderma spp
Abstract
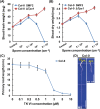
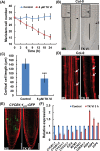
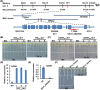
Trichoderma spp. are well known biocontrol agents that produce a variety of antibiotics. Peptaibols are a class of linear peptide antibiotics mainly produced by Trichoderma Alamethicin, the most studied peptaibol, is reported as toxic to plants at certain concentrations, while the mechanisms involved are unclear. We illustrated the toxic mechanisms of peptaibols by studying the growth-inhibitory effect of Trichokonin VI (TK VI), a peptaibol from Trichoderma longibrachiatum SMF2, on Arabidopsis primary roots. TK VI inhibited root growth by suppressing cell division and cell elongation, and disrupting root stem cell niche maintenance. TK VI increased auxin content and disrupted auxin response gradients in root tips. Further, we screened the Arabidopsis TK VI-resistant mutant tkr1. tkr1 harbors a point mutation in GORK, which encodes gated outwardly rectifying K(+)channel proteins. This mutation alleviated TK VI-induced suppression of K(+)efflux in roots, thereby stabilizing the auxin gradient. The tkr1 mutant also resisted the phytotoxicity of alamethicin. Our results indicate that GORK channels play a key role in peptaibol-plant interaction and that there is an inter-relationship between GORK channels and maintenance of auxin homeostasis. The cellular and molecular insight into the peptaibol-induced inhibition of plant root growth advances our understanding of Trichoderma-plant interactions.
Keywords: Arabidopsis thaliana; GORK; Trichoderma; Trichokonin VI.; auxin; peptaibols.
© The Author 2016. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Society for Experimental Biology.
Figures






References
-
- Ache P, Becker D, Ivashikina N, Dietrich P, Roelfsema MRG, Hedrich R. 2000. GORK, a delayed outward rectifier expressed in guard cells of Arabidopsis thaliana, is a K+-selective, K+-sensing ion channel. FEBS Letters 486, 93–98. - PubMed
-
- Aida M, Beis D, Heidstra R, Willemsen V, Blilou I, Galinha C, Nussaume L, Noh YS, Amasino R, Scheres B. 2004. The PLETHORA genes mediate patterning of the Arabidopsis root stem cell niche. Cell 119, 109–120. - PubMed
-
- Bechtold N, Pelletier G. 1998. In planta Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of adult Arabidopsis thaliana plants by vacuum infiltration. Methods in Molecular Biology 82, 259–266. - PubMed
-
- Benítez T, Rincón AM, Limón MC, Codón AC. 2004. Biocontrol mechanisms of Trichoderma strains. International Microbiology 7, 249–260. - PubMed
-
- Béven L, Helluin O, Molle G, Duclohier H, Wróblewski H. 1999. Correlation between anti-bacterial activity and pore-sizes of two classes of voltage-dependent channel-forming peptides. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta 1420, 53–63. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

