UHRF1 regulation of Dnmt1 is required for pre-gastrula zebrafish development
- PMID: 26851214
- PMCID: PMC4814311
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2016.01.036
UHRF1 regulation of Dnmt1 is required for pre-gastrula zebrafish development
Abstract
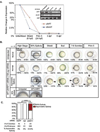
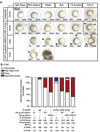
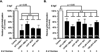
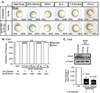
Landmark epigenetic events underlie early embryonic development, yet how epigenetic modifiers are regulated to achieve rapid epigenome re-patterning is not known. Uhrf1 and DNA methyltransferase 1 (Dnmt1) are known to largely mediate maintenance DNA methylation and Uhrf1 is also required for both Dnmt1 localization and stability. Here, we investigate how these two key epigenetic modifiers regulate early zebrafish development and characterize the developmental consequences of disrupting their homeostatic relationship. Unlike Uhrf1 knockdown, which causes developmental arrest and death prior to gastrulation, overexpression of human UHRF1 (WT-UHRF1) caused asymmetric epiboly, inefficient gastrulation and multi-systemic defects. UHRF1 phosphorylation was previously demonstrated as essential for zebrafish embryogenesis, and we found that penetrance of the asymmetric epiboly phenotype was significantly increased in embryos injected with mRNA encoding non-phosphorylatable UHRF1 (UHRF1(S661A)). Surprisingly, both WT-UHRF1 and UHRF1(S661A) overexpression caused DNA hypomethylation. However, since other approaches that caused an equivalent degree of DNA hypomethylation did not cause the asymmetric epiboly phenotype, we conclude that bulk DNA methylation is not the primary mechanism. Instead, UHRF1(S661A) overexpression resulted in accumulation of Dnmt1 protein and the overexpression of both WT and a catalytically inactive Dnmt1 phenocopied the assymetric epiboly phenotype. Dnmt1 knockdown suppressed the phenotype caused by UHRF1(S661A) overexpression, and Uhrf1 knockdown suppressed the effect of Dnmt1 overexpression. Therefore, we conclude that the interaction between these two proteins is the mechanism underlying the gastrulation defects. This indicates that Dnmt1 stability requires UHRF1 phosphorylation and that crosstalk between the proteins is essential for the function of these two important epigenetic regulators during gastrulation.
Keywords: DNA methylation; Dnmt1; Epiboly; Epigenetics; Uhrf1; Zebrafish development.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures




References
-
- Arita K, Ariyoshi M, Tochio H, Nakamura Y, Shirakawa M. Recognition of hemi-methylated DNA by the SRA protein UHRF1 by a base-flipping mechanism. Nature. 2008;455:818–821. - PubMed
-
- Arita K, Isogai S, Oda T, Unoki M, Sugita K, Sekiyama N, Kuwata K, Hamamoto R, Tochio H, Sato M, et al. Recognition of modification status on a histone H3 tail by linked histone reader modules of the epigenetic regulator UHRF1. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 2012;109:12950–12955. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Avvakumov GV, Walker JR, Xue S, Li Y, Duan S, Bronner C, Arrowsmith CH, Dhe-Paganon S. Structural basis for recognition of hemi-methylated DNA by the SRA domain of human UHRF1. Nature. 2008;455:822–825. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

