Downregulation of histone H2A and H2B pathways is associated with anthracycline sensitivity in breast cancer
- PMID: 26852132
- PMCID: PMC4744406
- DOI: 10.1186/s13058-016-0676-6
Downregulation of histone H2A and H2B pathways is associated with anthracycline sensitivity in breast cancer
Abstract
Background: Drug resistance in breast cancer is the major obstacle to effective treatment with chemotherapy. While upregulation of multidrug resistance genes is an important component of drug resistance mechanisms in vitro, their clinical relevance remains to be determined. Therefore, identifying pathways that could be targeted in the clinic to eliminate anthracycline-resistant breast cancer remains a major challenge.
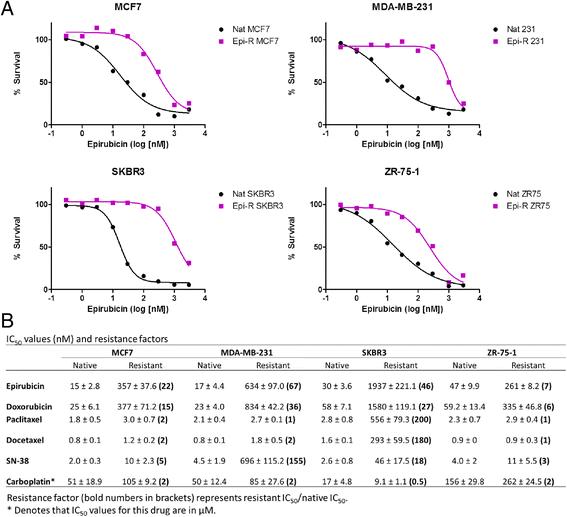
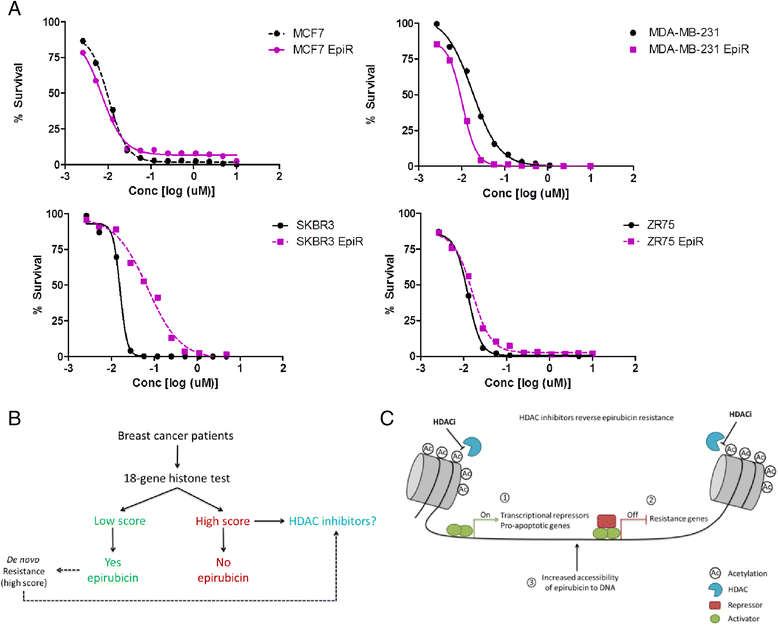
Methods: We generated paired native and epirubicin-resistant MDA-MB-231, MCF7, SKBR3 and ZR-75-1 epirubicin-resistant breast cancer cell lines to identify pathways contributing to anthracycline resistance. Native cell lines were exposed to increasing concentrations of epirubicin until resistant cells were generated. To identify mechanisms driving epirubicin resistance, we used a complementary approach including gene expression analyses to identify molecular pathways involved in resistance, and small-molecule inhibitors to reverse resistance. In addition, we tested its clinical relevance in a BR9601 adjuvant clinical trial.
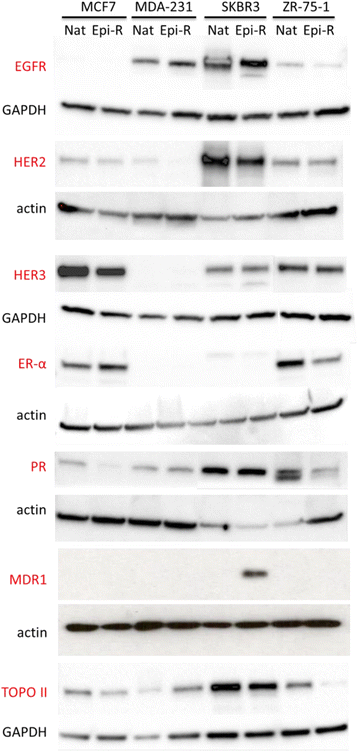
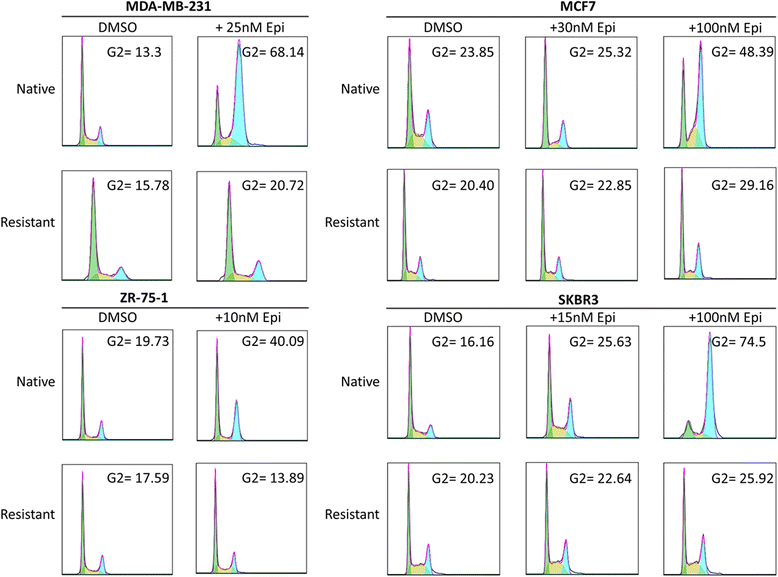
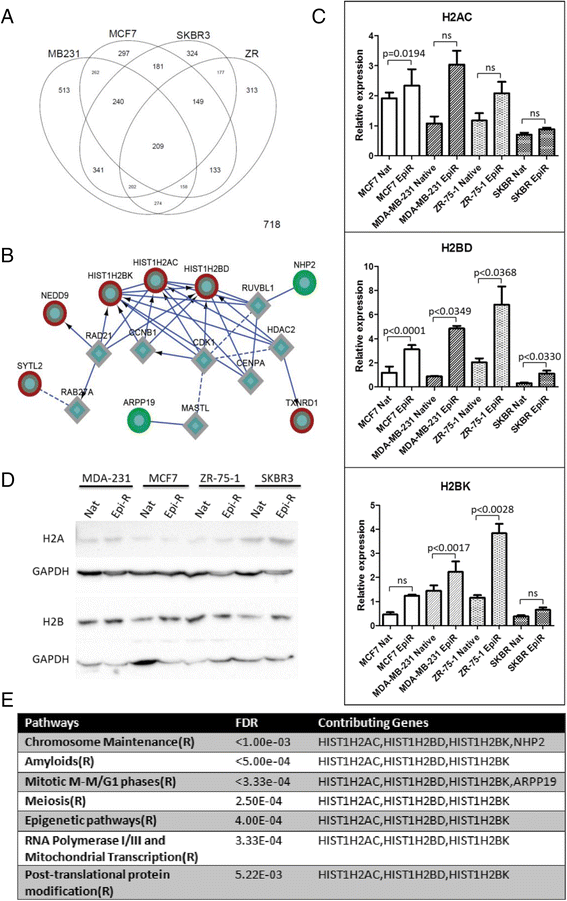
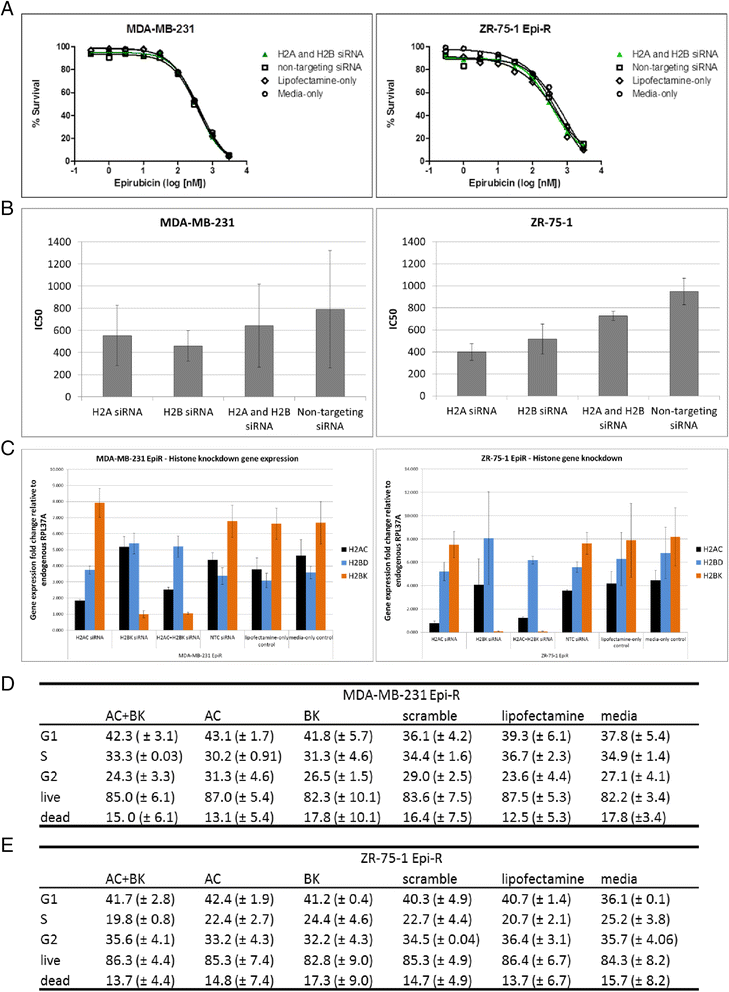
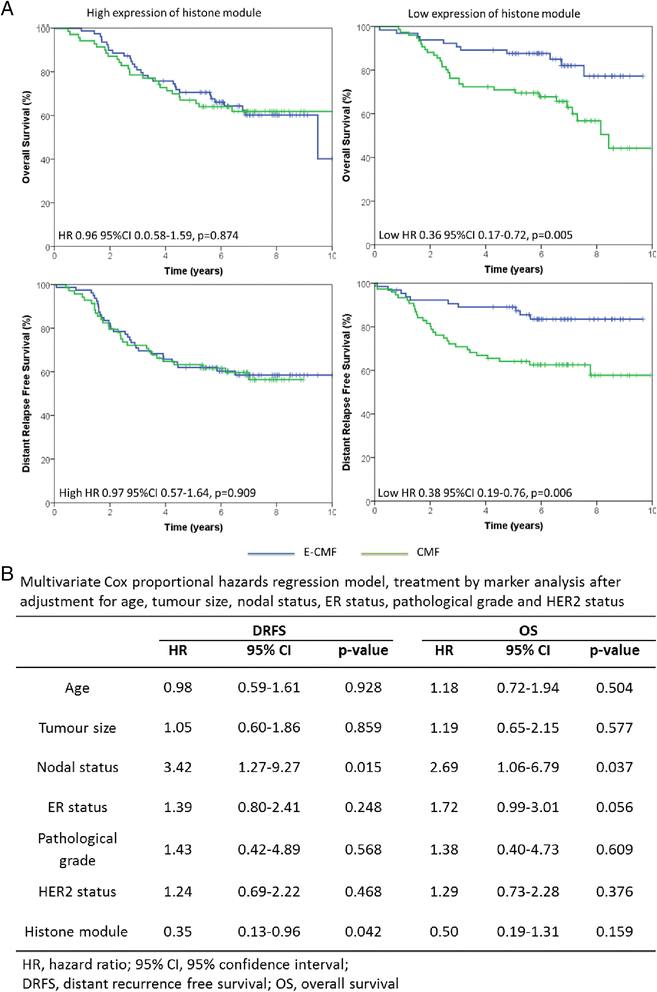
Results: Characterisation of epirubicin-resistant cells revealed that they were cross-resistant to doxorubicin and SN-38 and had alterations in apoptosis and cell-cycle profiles. Gene expression analysis identified deregulation of histone H2A and H2B genes in all four cell lines. Histone deacetylase small-molecule inhibitors reversed resistance and were cytotoxic for epirubicin-resistant cell lines, confirming that histone pathways are associated with epirubicin resistance. Gene expression of a novel 18-gene histone pathway module analysis of the BR9601 adjuvant clinical trial revealed that patients with low expression of the 18-gene histone module benefited from anthracycline treatment more than those with high expression (hazard ratio 0.35, 95 % confidence interval 0.13-0.96, p = 0.042).
Conclusions: This study revealed a key pathway that contributes to anthracycline resistance and established model systems for investigating drug resistance in all four major breast cancer subtypes. As the histone modification can be targeted with small-molecule inhibitors, it represents a possible means of reversing clinical anthracycline resistance.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov identifier NCT00003012 . Registered on 1 November 1999.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Alterations in estrogen signalling pathways upon acquisition of anthracycline resistance in breast tumor cells.PLoS One. 2017 Feb 14;12(2):e0172244. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0172244. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28196134 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular characterization of irinotecan (SN-38) resistant human breast cancer cell lines.BMC Cancer. 2016 Jan 22;16:34. doi: 10.1186/s12885-016-2071-1. BMC Cancer. 2016. PMID: 26801902 Free PMC article.
-
Histone deacetylase inhibitor reverses multidrug resistance by attenuating the nucleophosmin level through PI3K/Akt pathway in breast cancer.Int J Oncol. 2016 Jul;49(1):294-304. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2016.3528. Epub 2016 May 17. Int J Oncol. 2016. PMID: 27211281
-
[Anthracyclines in the adjuvant treatment of breast carcinoma: thirty years later].Clin Ter. 2006 Mar-Apr;157(2):165-77. Clin Ter. 2006. PMID: 16817507 Review. Italian.
-
Reflections on the development of resistance during therapy for advanced breast cancer. Implications of high levels of activity of docetaxel in anthracycline-resistant breast cancer patients.Eur J Cancer. 1997 Aug;33 Suppl 7:S7-10. doi: 10.1016/s0959-8049(97)90002-2. Eur J Cancer. 1997. PMID: 9486096 Review.
Cited by
-
DoxoDB: A Database for the Expression Analysis of Doxorubicin-Induced lncRNA Genes.Noncoding RNA. 2023 Jul 13;9(4):39. doi: 10.3390/ncrna9040039. Noncoding RNA. 2023. PMID: 37489459 Free PMC article.
-
Proteomic Analysis on Anti-Proliferative and Apoptosis Effects of Curcumin Analog, 1,5-bis(4-Hydroxy-3-Methyoxyphenyl)-1,4-Pentadiene-3-One-Treated Human Glioblastoma and Neuroblastoma Cells.Front Mol Biosci. 2021 Apr 30;8:645856. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2021.645856. eCollection 2021. Front Mol Biosci. 2021. PMID: 33996900 Free PMC article.
-
Chemotherapy induces ACE2 expression in breast cancer via the ROS-AKT-HIF-1α signaling pathway: a potential prognostic marker for breast cancer patients receiving chemotherapy.J Transl Med. 2022 Nov 5;20(1):509. doi: 10.1186/s12967-022-03716-w. J Transl Med. 2022. PMID: 36335375 Free PMC article.
-
Canady Helios Cold Plasma Induces Breast Cancer Cell Death by Oxidation of Histone mRNA.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Sep 3;22(17):9578. doi: 10.3390/ijms22179578. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34502492 Free PMC article.
-
HDAC inhibition as a treatment concept to combat temsirolimus-resistant bladder cancer cells.Oncotarget. 2017 Nov 6;8(66):110016-110028. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.22454. eCollection 2017 Dec 15. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 29299126 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Guo B, Villeneuve DJ, Hembruff SL, Kirwan AF, Blais DE, Bonin M, et al. Cross-resistance studies of isogenic drug-resistant breast tumor cell lines support recent clinical evidence suggesting that sensitivity to paclitaxel may be strongly compromised by prior doxorubicin exposure. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2004;85:31–51. doi: 10.1023/B:BREA.0000021046.29834.12. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Chazard M, Pellae-Cosset B, Garet F, Soares JA, Lucidi B, Lavail Y, et al. Taxol (paclitaxel), first molecule of a new class of cytotoxic agents: taxanes. Bull Cancer. 1994;81:173–181. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

