The cost of cancer: a retrospective analysis of the financial impact of cancer on young adults
- PMID: 26853096
- PMCID: PMC4864815
- DOI: 10.1002/cam4.657
The cost of cancer: a retrospective analysis of the financial impact of cancer on young adults
Abstract
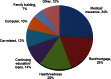
Young adult cancer survivors (YAs) are confronted with immense financial challenges in the wake of their treatment. Medical bills and loss of savings may cause YAs to forgo recommended medications or follow-up appointments. Young survivors with financial concerns also report depression, stress and anxiety. The Samfund is a national nonprofit organization that provides financial support to YAs post-treatment. To quantify the financial burden of cancer in YAs, a retrospective analysis was performed of data collected from Samfund grant applications of 334 YA cancer survivors. Grants were awarded between 2007 and 2013 and grant recipients were consented electronically in 2014 for retrospective data analysis. Recipients ranged from 19 to 39 years of age at the time of their grant applications. Descriptive statistics were calculated and compared to the Medical Expenditure Panel Survey (MEPS) and U.S. census data on age-matched peers. Financial indicators of YA cancer survivors are worse in many domains than those of age-matched controls. Furthermore, YA survivors in their 30s report more perilous prefunding financial situations than younger grant recipients. Cancer has a devastating and age-specific impact on the finances of YAs. Philanthropic grants from the cancer support community, in conjunction with healthcare policy reforms, have the potential to break the cycle of financial need and help YAs move forward with their lives after cancer treatment.
Keywords: Cancer; cost of illness; financial support; health expenditures; young adult.
© 2016 The Authors. Cancer Medicine published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

