Crystal Structures of Type-II Inositol Polyphosphate 5-Phosphatase INPP5B with Synthetic Inositol Polyphosphate Surrogates Reveal New Mechanistic Insights for the Inositol 5-Phosphatase Family
- PMID: 26854536
- PMCID: PMC4785718
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.biochem.5b00838
Crystal Structures of Type-II Inositol Polyphosphate 5-Phosphatase INPP5B with Synthetic Inositol Polyphosphate Surrogates Reveal New Mechanistic Insights for the Inositol 5-Phosphatase Family
Abstract
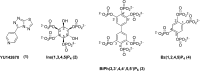
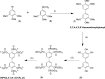
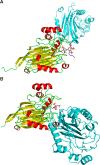
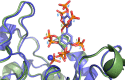
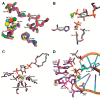
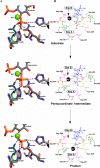
The inositol polyphosphate 5-phosphatase INPP5B hydrolyzes the 5-phosphate group from water- and lipid-soluble signaling messengers. Two synthetic benzene and biphenyl polyphosphates (BzP/BiPhPs), simplified surrogates of inositol phosphates and phospholipid headgroups, were identified by thermodynamic studies as potent INPP5B ligands. The X-ray structure of the complex between INPP5B and biphenyl 3,3',4,4',5,5'-hexakisphosphate [BiPh(3,3',4,4',5,5')P6, IC50 5.5 μM] was determined at 2.89 Å resolution. One inhibitor pole locates in the phospholipid headgroup binding site and the second solvent-exposed ring binds to the His-Tag of another INPP5B molecule, while a molecule of inorganic phosphate is also present in the active site. Benzene 1,2,3-trisphosphate [Bz(1,2,3)P3] [one ring of BiPh(3,3',4,4',5,5')P6] inhibits INPP5B ca. 6-fold less potently. Co-crystallization with benzene 1,2,4,5-tetrakisphosphate [Bz(1,2,4,5)P4, IC50 = 6.3 μM] yielded a structure refined at 2.9 Å resolution. Conserved residues among the 5-phosphatase family mediate interactions with Bz(1,2,4,5)P4 and BiPh(3,3',4,4',5,5')P6 similar to those with the polar groups present in positions 1, 4, 5, and 6 on the inositol ring of the substrate. 5-Phosphatase specificity most likely resides in the variable zone located close to the 2- and 3-positions of the inositol ring, offering insights to inhibitor design. We propose that the inorganic phosphate present in the INPP5B-BiPh(3,3',4,4',5,5')P6 complex mimics the postcleavage substrate 5-phosphate released by INPP5B in the catalytic site, allowing elucidation of two new key features in the catalytic mechanism proposed for the family of phosphoinositide 5-phosphatases: first, the involvement of the conserved Arg-451 in the interaction with the 5-phosphate and second, identification of the water molecule that initiates 5-phosphate hydrolysis. Our model also has implications for the proposed "moving metal" mechanism.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures

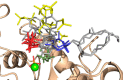
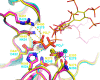
Similar articles
-
Structural basis for phosphoinositide substrate recognition, catalysis, and membrane interactions in human inositol polyphosphate 5-phosphatases.Structure. 2014 May 6;22(5):744-55. doi: 10.1016/j.str.2014.01.013. Epub 2014 Apr 3. Structure. 2014. PMID: 24704254
-
Specificity determinants in phosphoinositide dephosphorylation: crystal structure of an archetypal inositol polyphosphate 5-phosphatase.Cell. 2001 May 4;105(3):379-89. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(01)00326-9. Cell. 2001. PMID: 11348594
-
Benzene polyphosphates as tools for cell signalling: inhibition of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate 5-phosphatase and interaction with the PH domain of protein kinase Balpha.Chembiochem. 2008 Jul 21;9(11):1757-66. doi: 10.1002/cbic.200800104. Chembiochem. 2008. PMID: 18574825 Free PMC article.
-
Structural analyses of inositol phosphate second messengers bound to signaling effector proteins.Adv Biol Regul. 2020 Jan;75:100667. doi: 10.1016/j.jbior.2019.100667. Epub 2019 Oct 11. Adv Biol Regul. 2020. PMID: 31648945 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ins(1,4,5)P3 metabolism and the family of IP3-3Kinases.Cell Signal. 2004 Jun;16(6):643-54. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2003.10.009. Cell Signal. 2004. PMID: 15093605 Review.
Cited by
-
Allosteric Site on SHIP2 Identified Through Fluorescent Ligand Screening and Crystallography: A Potential New Target for Intervention.J Med Chem. 2021 Apr 8;64(7):3813-3826. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.0c01944. Epub 2021 Mar 16. J Med Chem. 2021. PMID: 33724834 Free PMC article.
-
Inferring joint sequence-structural determinants of protein functional specificity.Elife. 2018 Jan 16;7:e29880. doi: 10.7554/eLife.29880. Elife. 2018. PMID: 29336305 Free PMC article.
-
Genotype & phenotype in Lowe Syndrome: specific OCRL1 patient mutations differentially impact cellular phenotypes.Hum Mol Genet. 2021 Apr 26;30(3-4):198-212. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddab025. Hum Mol Genet. 2021. PMID: 33517444 Free PMC article.
-
Structural basis for interdomain communication in SHIP2 providing high phosphatase activity.Elife. 2017 Aug 9;6:e26640. doi: 10.7554/eLife.26640. Elife. 2017. PMID: 28792888 Free PMC article.
-
Aminocholestane and Aminoandrostane Inhibitors of the SH2 Domain-Containing Inositol 5'-Phosphatase (SHIP).ChemMedChem. 2025 Apr 14;20(8):e202400597. doi: 10.1002/cmdc.202400597. Epub 2025 Feb 13. ChemMedChem. 2025. PMID: 39843392
References
-
- Mills S. J.; Persson C.; Cozier G.; Thomas M. P.; Trésaugues L.; Erneux C.; Riley A. M.; Nordlund P.; Potter B. V. L. (2012) A synthetic polyphosphoinositide headgroup surrogate in complex with SHIP2 provides a rationale for drug discovery. ACS Chem. Biol. 7, 822–828. 10.1021/cb200494d. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

