C. elegans lifespan extension by osmotic stress requires FUdR, base excision repair, FOXO, and sirtuins
- PMID: 26854551
- PMCID: PMC4789167
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mad.2016.01.004
C. elegans lifespan extension by osmotic stress requires FUdR, base excision repair, FOXO, and sirtuins
Abstract
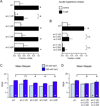
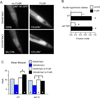
Moderate stress can increase lifespan by hormesis, a beneficial low-level induction of stress response pathways. 5'-fluorodeoxyuridine (FUdR) is commonly used to sterilize Caenorhabditis elegans in aging experiments. However, FUdR alters lifespan in some genotypes and induces resistance to thermal and proteotoxic stress. We report that hypertonic stress in combination with FUdR treatment or inhibition of the FUdR target thymidylate synthase, TYMS-1, extends C. elegans lifespan by up to 30%. By contrast, in the absence of FUdR, hypertonic stress decreases lifespan. Adaptation to hypertonic stress requires diminished Notch signaling and loss of Notch co-ligands leads to lifespan extension only in combination with FUdR. Either FUdR treatment or TYMS-1 loss induced resistance to acute hypertonic stress, anoxia, and thermal stress. FUdR treatment increased expression of DAF-16 FOXO and the osmolyte biosynthesis enzyme GPDH-1. FUdR-induced hypertonic stress resistance was partially dependent on sirtuins and base excision repair (BER) pathways, while FUdR-induced lifespan extension under hypertonic stress conditions requires DAF-16, BER, and sirtuin function. Combined, these results demonstrate that FUdR, through inhibition of TYMS-1, activates stress response pathways in somatic tissues to confer hormetic resistance to acute and chronic stress. C. elegans lifespan studies using FUdR may need re-interpretation in light of this work.
Keywords: C. elegans; FOXO; FUdR; Hormesis; Hypertonic stress; Sirtuin.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Ireland Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Aitlhadj L, Stürzenbaum SR. The use of FUdR can cause prolonged longevity in mutant nematodes. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2010;131:364–365. - PubMed
-
- Arantes-Oliveira N, Apfeld J, Dillin A, Kenyon C. Regulation of life-span by germ-line stem cells in Caenorhabditis elegans . Science. 2002;295:502–505. - PubMed
-
- Arum O, Johnson TE. Reduced Expression of the Caenorhabditis elegans p53 Ortholog cep-1 Results in Increased Longevity. Journals Gerontol. Ser. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2007;62:951–959. - PubMed
-
- Brunquell J, Bowers P, Westerheide SD. Fluorodeoxyuridine enhances the heat shock response and decreases polyglutamine aggregation in an HSF-1-dependent manner in Caenorhabditis elegans . Mech. Ageing Dev. 2014:8–11. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

