Advances in microfluidics in combating infectious diseases
- PMID: 26854743
- PMCID: PMC7125941
- DOI: 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2016.02.002
Advances in microfluidics in combating infectious diseases
Abstract
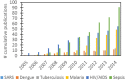
One of the important pursuits in science and engineering research today is to develop low-cost and user-friendly technologies to improve the health of people. Over the past decade, research efforts in microfluidics have been made to develop methods that can facilitate low-cost diagnosis of infectious diseases, especially in resource-poor settings. Here, we provide an overview of the recent advances in microfluidic devices for point-of-care (POC) diagnostics for infectious diseases and emphasis is placed on malaria, sepsis and AIDS/HIV. Other infectious diseases such as SARS, tuberculosis, and dengue are also briefly discussed. These infectious diseases are chosen as they contribute the most to disability-adjusted life-years (DALYs) lost according to the World Health Organization (WHO). The current state of research in this area is evaluated and projection toward future applications and accompanying challenges are also discussed.
Keywords: Diagnostics; HIV; Infectious diseases; Malaria; Microfluidics; Point-of-care; Sepsis.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures





References
-
- Aceti A., Bonincontro A., Cametti C., Celestino D., Leri O. Electrical conductivity of human erythrocytes infected with Plasmodium falciparum and its modification following quinine therapy. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1990;84(5):671–672. ([Internet]. Jan [cited 2015 Mar 1] Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/2278066) - PubMed
-
- Aeinehvand M.M., Ibrahim F., Harun S.W., Djordjevic I., Hosseini S., Rothan H.A. Biosensing enhancement of dengue virus using microballoon mixers on centrifugal microfluidic platforms. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015;67:424–430. ([Internet]. May 15 [cited 2015 May 6] Available from: http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0956566314006721) - PubMed
-
- Aird W.C. Sepsis and coagulation. Crit. Care Clin. 2005:417–431. - PubMed
-
- Alizadehrad D., Imai Y., Nakaaki K., Ishikawa T., Yamaguchi T. Quantification of red blood cell deformation at high-hematocrit blood flow in microvessels. J. Biomech. 2012;45:2684–2689. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

