Analysis of the role of the LH92_11085 gene of a biofilm hyper-producing Acinetobacter baumannii strain on biofilm formation and attachment to eukaryotic cells
- PMID: 26854744
- PMCID: PMC4871663
- DOI: 10.1080/21505594.2016.1145335
Analysis of the role of the LH92_11085 gene of a biofilm hyper-producing Acinetobacter baumannii strain on biofilm formation and attachment to eukaryotic cells
Abstract
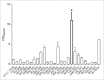
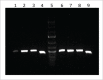
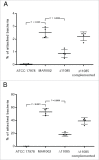
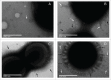
Acinetobacter baumannii is a nosocomial pathogen that has a considerable ability to survive in the hospital environment partly due to its capacity to form biofilms. The first step in the process of establishing an infection is adherence of the bacteria to target cells. Chaperone-usher pili assembly systems are involved in pilus biogenesis pathways that play an important role in adhesion to host cells and tissues as well as medically relevant surfaces. After screening a collection of strains, a biofilm hyper-producing A. baumannii strain (MAR002) was selected to describe potential targets involved in pathogenicity. MAR002 showed a remarkable ability to form biofilm and attach to A549 human alveolar epithelial cells. Analysis of MAR002 using transmission electron microscopy (TEM) showed a significant presence of pili on the bacterial surface. Putative protein-coding genes involved in pili formation were identified based on the newly sequenced genome of MAR002 strain (JRHB01000001/2 or NZ_JRHB01000001/2). As assessed by qRT-PCR, the gene LH92_11085, belonging to the operon LH92_11070-11085, is overexpressed (ca. 25-fold more) in biofilm-associated cells compared to exponential planktonic cells. In the present work we investigate the role of this gene on the MAR002 biofilm phenotype. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and biofilm assays showed that inactivation of LH92_11085 gene significantly reduced bacterial attachment to A549 cells and biofilm formation on plastic, respectively. TEM analysis of the LH92_11085 mutant showed the absence of long pili formations normally present in the wild-type. These observations indicate the potential role this LH92_11085 gene could play in the pathobiology of A baumannii.
Keywords: acinetobacter baumannii; attachment; biofilm; pathogenicity; pili; virulence.
Figures


Comment in
-
Acinetobacter baumannii virulence determinants involved in biofilm growth and adherence to host epithelial cells.Virulence. 2016 May 18;7(4):367-8. doi: 10.1080/21505594.2016.1150405. Epub 2016 Feb 8. Virulence. 2016. PMID: 26856342 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Peleg AY, Seifert H, Paterson DL. Acinetobacter baumannii: emergence of a successful pathogen. Clin Microbiol Rev 2008; 21:538–82; PMID:18625687; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1128/CMR.00058-07 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Dijkshoorn L, Nemec A, Seifert H. An increasing threat in hospitals: multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. Nat Rev Microbiol 2007; 5:939–51; PMID:18007677; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1038/nrmicro1789 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ong CW, Lye DC, Khoo KL, Chua GS, Yeoh SF, Leo YS, Tambyah PA, Chua AC. Severe community-acquired Acinetobacter baumannii pneumonia: an emerging highly lethal infectious disease in the Asia-Pacific. Respirology 2009; 14:1200–5; PMID:19909464; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1111/j.1440-1843.2009.01630.x - DOI - PubMed
-
- Merino M, Alvarez-Fraga L, Gomez MJ, Aransay AM, Lavin JL, Chaves F, Bou G, Poza M. Complete Genome Sequence of the Multiresistant Acinetobacter baumannii Strain AbH12O-A2, Isolated during a Large Outbreak in Spain. Genome Announc 2014; 2:e01182-14; PMID:25395646; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1128/genomeA.01182-14 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- del Mar Tomas M, Cartelle M, Pertega S, Beceiro A, Llinares P, Canle D, Molina F, Villanueva R, Cisneros JM, Bou G. Hospital outbreak caused by a carbapenem-resistant strain of Acinetobacter baumannii: patient prognosis and risk-factors for colonisation and infection. Clin Microbiol Infect 2005; 11:540–6; PMID:15966971; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1111/j.1469-0691.2005.01184.x - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
