Validity of SenseWear® Armband v5.2 and v2.2 for estimating energy expenditure
- PMID: 26854829
- PMCID: PMC5047752
- DOI: 10.1080/02640414.2016.1140220
Validity of SenseWear® Armband v5.2 and v2.2 for estimating energy expenditure
Abstract
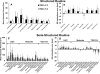
We compared SenseWear Armband versions (v) 2.2 and 5.2 for estimating energy expenditure in healthy adults. Thirty-four adults (26 women), 30.1 ± 8.7 years old, performed two trials that included light-, moderate- and vigorous-intensity activities: (1) structured routine: seven activities performed for 8-min each, with 4-min of rest between activities; (2) semi-structured routine: 12 activities performed for 5-min each, with no rest between activities. Energy expenditure was measured by indirect calorimetry and predicted using SenseWear v2.2 and v5.2. Compared to indirect calorimetry (297.8 ± 54.2 kcal), the total energy expenditure was overestimated (P < 0.05) by both SenseWear v2.2 (355.6 ± 64.3 kcal) and v5.2 (342.6 ± 63.8 kcal) during the structured routine. During the semi-structured routine, the total energy expenditure for SenseWear v5.2 (275.2 ± 63.0 kcal) was not different than indirect calorimetry (262.8 ± 52.9 kcal), and both were lower (P < 0.05) than v2.2 (312.2 ± 74.5 kcal). The average mean absolute per cent error was lower for the SenseWear v5.2 than for v2.2 (P < 0.001). SenseWear v5.2 improved energy expenditure estimation for some activities (sweeping, loading/unloading boxes, walking), but produced larger errors for others (cycling, rowing). Although both algorithms overestimated energy expenditure as well as time spent in moderate-intensity physical activity (P < 0.05), v5.2 offered better estimates than v2.2.
Keywords: Activity monitor; accelerometer; assessment; calorimetry; physical activity.
Figures


References
-
- Ainsworth BE, Haskell WL, Herrmann SD, Meckes N, Bassett DR, Tudor-Locke C, Leon AS. 2011 compendium of physical activities: a second update of codes and MET values. Medicine and Science in Sports and Exercise. 2011;43(8):1575–1581. - PubMed
-
- Benito P, Neiva C, Gonzalez-Quijano P, Cupeiro R, Morencos E, Peinado A. Validation of the SenseWear armband in circuit resistance training with different loads. European Journal of Applied Physiology. 2012;112(8):3155–3159. - PubMed
-
- Berntsen S, Hageberg R, Aandstad A, Mowinckel P, Anderssen SA, Carlsen KH, Andersen LB. Validity of physical activity monitors in adults participating in free-living activities. British Journal of Sports Medicine. 2010;44(9):657–664. doi: 10.1136/bjsm.2008.048868. - PubMed
-
- Bhammar DM, Sawyer BJ, Tucker WJ, Baez JC, Gaesser GA. Actiheart and Actigraph in Adults Poster session presented at the meeting of the American College of Sports Medicine. Indianapolis, IN.: May, 2013. Physical Activity and Energy Expenditure Measurements Using Sensewear Armband.
-
- Bland JM, Altman DG. Statistical-Methods for Assessing Agreement between 2 Methods of Clinical Measurement. Lancet. 1986;1(8476) - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
