Fatal outcome of human coronavirus NL63 infection despite successful viral elimination by IFN-alpha in a patient with newly diagnosed ALL
- PMID: 26854965
- PMCID: PMC7163643
- DOI: 10.1111/ejh.12744
Fatal outcome of human coronavirus NL63 infection despite successful viral elimination by IFN-alpha in a patient with newly diagnosed ALL
Abstract
Introduction: Human coronavirus NL63 (HCoV-NL63) is one of four common human respiratory coronaviruses. Despite high incidence, HCoV infections are grossly understudied. We here report a case of HCoV infection in a leukemia patient with fatal ARDS despite successful virus elimination by pegylated interferon-alpha (PEG-IFN-α).
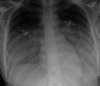
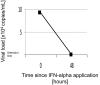
Case: The 27-year-old female pre-T-ALL patient was treated according to the German-Multicenter Trial for Adult ALL protocol. No relevant infectious complications were seen until day 35 when the neutropenic patient developed fever without any clinical focus. Antibiotic prophylaxis was switched to meropenem. The patient deteriorated rapidly with respiratory failure due to ARDS. Anti-infectious therapy was escalated to additional linezolid and liposomal amphotericine-B. BAL revealed a significant viral load of HCoV-NL63. Based on successful application of PEG-IFN against the related SARS coronavirus in animal experiments, a single injection of 180 μg PEG-IFN-α2b was applied. Despite immediate initiation of treatment and elimination of virus in subsequent tests, the progressive lung failure led to death 7 d after onset of fever with massive lung bleeding as a consequence of diffuse alveolar hemorrhage.
Conclusion: This report emphasizes the fatal consequences of common respiratory virus infections in immunocompromised patients. HCoV-NL63 replication can be reduced by treatment with peg-IFN if diagnosed early.
Keywords: ALL; ARDS; coronavirus.
© 2016 John Wiley & Sons A/S. Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Drosten C, Günther S, Preiser W, et al Identification of a novel coronavirus in patients with severe acute respiratory syndrome. N Engl J Med 2003;348:1967–76. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous