Structural Insight into Substrate Selectivity of Erwinia chrysanthemi L-asparaginase
- PMID: 26855287
- PMCID: PMC4776285
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.biochem.5b01351
Structural Insight into Substrate Selectivity of Erwinia chrysanthemi L-asparaginase
Abstract
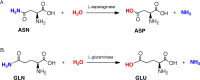
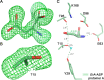
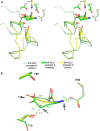
l-Asparaginases of bacterial origin are a mainstay of acute lymphoblastic leukemia treatment. The mechanism of action of these enzyme drugs is associated with their capacity to deplete the amino acid l-asparagine from the blood. However, clinical use of bacterial l-asparaginases is complicated by their dual l-asparaginase and l-glutaminase activities. The latter, even though representing only ∼10% of the overall activity, is partially responsible for the observed toxic side effects. Hence, l-asparaginases devoid of l-glutaminase activity hold potential as safer drugs. Understanding the key determinants of l-asparaginase substrate specificity is a prerequisite step toward the development of enzyme variants with reduced toxicity. Here we present crystal structures of the Erwinia chrysanthemi l-asparaginase in complex with l-aspartic acid and with l-glutamic acid. These structures reveal two enzyme conformations-open and closed-corresponding to the inactive and active states, respectively. The binding of ligands induces the positioning of the catalytic Thr15 into its active conformation, which in turn allows for the ordering and closure of the flexible N-terminal loop. Notably, l-aspartic acid is more efficient than l-glutamic acid in inducing the active positioning of Thr15. Structural elements explaining the preference of the enzyme for l-asparagine over l-glutamine are discussed with guidance to the future development of more specific l-asparaginases.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Structural basis for the activity and substrate specificity of Erwinia chrysanthemi L-asparaginase.Biochemistry. 2001 May 15;40(19):5655-64. doi: 10.1021/bi0029595. Biochemistry. 2001. PMID: 11341830
-
The differential ability of asparagine and glutamine in promoting the closed/active enzyme conformation rationalizes the Wolinella succinogenes L-asparaginase substrate specificity.Sci Rep. 2017 Jan 31;7:41643. doi: 10.1038/srep41643. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28139703 Free PMC article.
-
Atomic resolution structure of Erwinia chrysanthemi L-asparaginase.Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2003 Jan;59(Pt 1):84-92. doi: 10.1107/s0907444902019443. Epub 2002 Dec 19. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2003. PMID: 12499544
-
Asparaginase Erwinia chrysanthemi as a component of a multi-agent chemotherapeutic regimen for the treatment of patients with acute lymphoblastic leukemia who have developed hypersensitivity to E. coli-derived asparaginase.Expert Rev Hematol. 2016 Mar;9(3):227-34. doi: 10.1586/17474086.2016.1142370. Epub 2016 Feb 19. Expert Rev Hematol. 2016. PMID: 26765930 Review.
-
What makes a good new therapeutic L-asparaginase?World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2019 Sep 24;35(10):152. doi: 10.1007/s11274-019-2731-9. World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2019. PMID: 31552479 Review.
Cited by
-
Towards a dependable data set of structures for L-asparaginase research.Acta Crystallogr D Struct Biol. 2024 Jul 1;80(Pt 7):506-527. doi: 10.1107/S2059798324005461. Epub 2024 Jun 27. Acta Crystallogr D Struct Biol. 2024. PMID: 38935343 Free PMC article.
-
Thermostability Improvement of L-Asparaginase from Acinetobacter soli via Consensus-Designed Cysteine Residue Substitution.Molecules. 2022 Oct 7;27(19):6670. doi: 10.3390/molecules27196670. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36235209 Free PMC article.
-
Insights into the Distribution and Functional Properties of l-Asparaginase in the Archaeal Domain and Characterization of Picrophilus torridus Asparaginase Belonging to the Novel Family Asp2like1.ACS Omega. 2022 Nov 2;7(45):40750-40765. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.2c01127. eCollection 2022 Nov 15. ACS Omega. 2022. PMID: 36406543 Free PMC article.
-
Design and Characterization of Erwinia Chrysanthemi l-Asparaginase Variants with Diminished l-Glutaminase Activity.J Biol Chem. 2016 Aug 19;291(34):17664-76. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.728485. Epub 2016 Jun 27. J Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 27354283 Free PMC article.
-
Generalized enzymatic mechanism of catalysis by tetrameric L-asparaginases from mesophilic bacteria.Sci Rep. 2020 Oct 15;10(1):17516. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-74480-4. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 33060684 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Michalska K.; Jaskolski M. (2006) Structural aspects of l-asparaginases, their friends and relations. Acta Biochim Pol 53, 627–640. - PubMed
-
- Roberts J. (1976) Purification and properties of a highly potent antitumor glutaminase-asparaginase from Pseudomonas 7Z. J. Biol. Chem. 251, 2119–2123. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

