Tousled kinase activator, gallic acid, promotes homologous recombinational repair and suppresses radiation cytotoxicity in salivary gland cells
- PMID: 26855419
- PMCID: PMC5257199
- DOI: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2015.12.029
Tousled kinase activator, gallic acid, promotes homologous recombinational repair and suppresses radiation cytotoxicity in salivary gland cells
Abstract
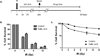
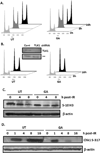
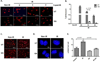
Accidental or medical radiation exposure of the salivary glands can gravely impact oral health. Previous studies have shown the importance of Tousled-like kinase 1 (TLK1) and its alternate start variant TLK1B in cell survival against genotoxic stresses. Through a high-throughput library screening of natural compounds, the phenolic phytochemical, gallic acid (GA), was identified as a modulator of TLK1/1B. This small molecule possesses anti-oxidant and free radical scavenging properties, but in this study, we report that in vitro it promotes survival of human salivary acinar cells, NS-SV-AC, through repair of ionizing radiation damage. Irradiated cells treated with GA show improved clonogenic survival compared to untreated controls. And, analyses of DNA repair kinetics by alkaline single-cell gel electrophoresis and γ-H2AX foci immunofluorescence indicate rapid resolution of DNA breaks in drug-treated cells. Study of DR-GFP transgene repair indicates GA facilitates homologous recombinational repair to establish a functional GFP gene. In contrast, inactivation of TLK1 or its shRNA knockdown suppressed resolution of radiation-induced DNA tails in NS-SV-AC, and homology directed repair in DR-GFP cells. Consistent with our results in culture, animals treated with GA after exposure to fractionated radiation showed better preservation of salivary function compared to saline-treated animals. Our results suggest that GA-mediated transient modulation of TLK1 activity promotes DNA repair and suppresses radiation cytoxicity in salivary gland cells.
Keywords: Acinar; DNA repair; Gallic acid; Homologous recombination; Radiation; Salivary; Tousled; Xerostomia.
Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
There is no conflict of interest to disclose.
Figures

References
-
- Li Y, DeFatta R, Anthony C, Sunavala G, De Benedetti A. A translationally regulated Tousled kinase phosphorylates histone H3 and confers radioresistance when overexpressed. Oncogene. 2001;20:726–738. - PubMed
-
- Silljé HH, Nigg EA. Identification of human Asf1 chromatin assembly factors as substrates of Tousled-like kinases. Curr Biol. 2001;11:1068–1073. - PubMed
-
- Sunavala-Dossabhoy G, De Benedetti A. Tousled homolog, TLK1, binds and phosphorylates Rad9; TLK1 acts as a molecular chaperone in DNA repair. DNA Repair (Amst) 2009;8:87–102. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

