Chemical and biological mechanisms of phytochemical activation of Nrf2 and importance in disease prevention
- PMID: 26855455
- PMCID: PMC4739799
- DOI: 10.1007/978-3-319-00581-2_7
Chemical and biological mechanisms of phytochemical activation of Nrf2 and importance in disease prevention
Abstract
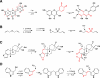
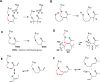
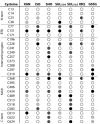
Plants are an incredibly rich source of compounds that activate the Nrf2 transcription factor, leading to upregulation of a battery of cytoprotective genes. This perspective surveys established and proposed molecular mechanisms of Nrf2 activation by phytochemicals with a special emphasis on a common chemical property of Nrf2 activators: the ability as "soft" electrophiles to modify cellular thiols, either directly or as oxidized biotransformants. In addition, the role of reactive oxygen/nitrogen species as secondary messengers in Nrf2 activation is discussed. While the uniquely reactive C151 of Keap1, an Nrf2 repressor protein, is highlighted as a key target of cytoprotective phytochemicals, also reviewed are other stress-responsive proteins, including kinases, which play non-redundant roles in the activation of Nrf2 by plant-derived agents. Finally, the perspective presents two key factors accounting for the enhanced therapeutic windows of effective phytochemical activators of the Keap1-Nrf2 axis: enhanced selectivity toward sensor cysteines and reversibility of addition to thiolate molecules.
Figures

References
-
- Kasai H, Kawai K. Oxidative DNA damage: mechanisms and significance in health and disease. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2006;8:981–983. - PubMed
-
- Malhotra D, Portales-Casamar E, Singh A, Srivastava S, Arenillas D, Happel C, Shyr C, Wakabayashi N, Kensler TW, Wasserman WW, Biswal S. Global mapping of binding sites for Nrf2 identifies novel targets in cell survival response through ChIP-Seq profiling and network analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010;38:5718–5734. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hayes JD, McMahon M. NRF2 and KEAP1 mutations: permanent activation of an adaptive response in cancer. Trends Biochem Sci. 2009;34:176–188. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
