Association between the Cyclin D1 G870A polymorphism and the susceptibility to and prognosis of upper aerodigestive tract squamous cell carcinomas: an updated meta-analysis
- PMID: 26855585
- PMCID: PMC4727518
- DOI: 10.2147/OTT.S94635
Association between the Cyclin D1 G870A polymorphism and the susceptibility to and prognosis of upper aerodigestive tract squamous cell carcinomas: an updated meta-analysis
Abstract
Purpose: Several publications have investigated the association between the Cyclin D1 G to A substitution at nucleotide 870 (CCND1 G870A) polymorphism and squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) of the upper aerodigestive tract (UADT), but their conclusions still remain controversial. We conducted a meta-analysis to precisely evaluate this association.
Patients and methods: We electronically searched the Chinese National Knowledge Infrastructure, PubMed, and Embase (up to January 2015) databases for case-control studies on the association between the CCND1 G870A polymorphism and SCC of the UADT, and 23 studies were included in total.
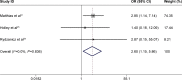
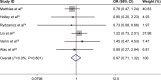
Results: The meta-analysis results showed that there was a significant association between the CCND1 G870A polymorphism and the risk of SCC of the UADT (AA vs GG: odds ratio [OR] =1.33, 95% confidence interval [CI] =1.01-1.74, P<0.001 for heterogeneity; GA/AA vs GG: OR =1.24, 95% CI =1.01-1.51, P<0.001 for heterogeneity; AA vs
Ga/gg: OR =1.16, 95% CI =0.97-1.39, P<0.001 for heterogeneity; allele A vs allele G: OR =1.14, 95% CI =1.00-1.30, P<0.001 for heterogeneity; GA vs GG: OR =1.18, 95% CI =0.98-1.42, P<0.001 for heterogeneity). However, when analyzing prognosis, allele G was a potential risk factor for poor tumor differentiation (AA vs
Ga/gg: OR =2.60, 95% CI =1.15-5.86, P=0.836 for heterogeneity) and reduced disease-free intervals (OR =2.08, 95% CI =1.17-3.69, P=0.134 for heterogeneity). In the subgroup analysis, the cancer susceptibility of Asian groups, population-based control groups, nasopharyngeal cancer groups, and esophageal SCC groups were more likely to be affected by the CCND1 G870A polymorphism. No significant publication bias was found in our analysis (P=0.961 for Egger's test and P=0.245 for Begg's test).
Conclusion: The results of the present meta-analysis suggest that the variant CCND1 870A allele might confer an elevated risk of SCC of the UADT, particularly among Asians and individuals who have esophageal or nasopharyngeal cancers. Moreover, the CCND1 870A allele might also confer better tumor differentiation grades and longer disease-free intervals.
Keywords: CCND1 G870A polymorphism; predictive value; screen; squamous cell carcinoma.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Cyclin D1 G870A polymorphism and risk of nasopharyngeal carcinoma: a case-control study and meta-analysis.PLoS One. 2014 Nov 19;9(11):e113299. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0113299. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25409185 Free PMC article.
-
CCND1 G870A polymorphism and colorectal cancer risk: An updated meta-analysis.Mol Clin Oncol. 2016 Jun;4(6):1078-1084. doi: 10.3892/mco.2016.844. Epub 2016 Apr 4. Mol Clin Oncol. 2016. PMID: 27284448 Free PMC article.
-
Association between cyclin D1 (CCND1) G870A polymorphism and gastric cancer risk: a meta-analysis.Oncotarget. 2016 Oct 4;7(40):66109-66118. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.11848. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27623072 Free PMC article.
-
AA genotype of cyclin D1 G870A polymorphism increases breast cancer risk: Findings of a case-control study and meta-analysis.J Cell Biochem. 2019 Oct;120(10):16452-16466. doi: 10.1002/jcb.28800. Epub 2019 Jun 26. J Cell Biochem. 2019. PMID: 31243808
-
The association between CCND1 G870A polymorphism and colorectal cancer risk: A meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2017 Oct;96(42):e8269. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000008269. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017. PMID: 29049220 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
PKC iota promotes cellular proliferation by accelerated G1/S transition via interaction with CDK7 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.Tumour Biol. 2016 Oct;37(10):13799-13809. doi: 10.1007/s13277-016-5193-9. Epub 2016 Aug 1. Tumour Biol. 2016. PMID: 27481515
-
Aberrant Cyclin D1 splicing in cancer: from molecular mechanism to therapeutic modulation.Cell Death Dis. 2023 Apr 6;14(4):244. doi: 10.1038/s41419-023-05763-7. Cell Death Dis. 2023. PMID: 37024471 Free PMC article. Review.
-
G870A Polymorphic Variants of CCND1 Gene and Cyclin D1 Protein Expression as Prognostic Markers in Laryngeal Lesions.Diagnostics (Basel). 2022 Apr 23;12(5):1059. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics12051059. Diagnostics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35626215 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cooper JS, Porter K, Mallin K, et al. National Cancer Database report on cancer of the head and neck: 10-year update. Head Neck. 2009;31(6):748–758. - PubMed
-
- Sherr CJ. Cancer cell cycles. Science. 1996;274(5293):1672–1677. - PubMed
-
- Jovanovic IP, Radosavljevic GD, Simovic-Markovic BJ, et al. Clinical significance of Cyclin D1, FGF3 and p21 protein expression in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma. J BUON. 2014;19(4):944–952. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

