Combination of siRNA-directed gene silencing with epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) reverses drug resistance in human breast cancer cells
- PMID: 26855680
- PMCID: PMC4733072
- DOI: 10.1007/s12154-015-0144-2
Combination of siRNA-directed gene silencing with epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) reverses drug resistance in human breast cancer cells
Abstract
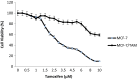
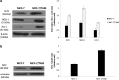
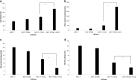
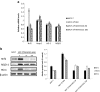
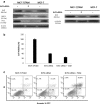
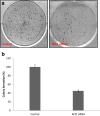
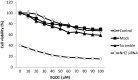
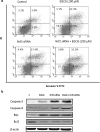
Elevated expression of NF-E2-related factor 2 (Nrf2), a nuclear transcription factor, is a frequent genetic abnormality seen in this malignancy and is an important contributor to chemoresistance in cancer therapy. In the present study, we investigated if Nrf2 was associated with drug resistance in tamoxifen-resistant MCF-7 (MCF-7/TAM) cells, and whether EGCG, major flavonoid isolated from green tea, could reverse drug resistance in MCF-7/TAM cells. Our results showed that the endogenous expression of Nrf2 as well as its target proteins heme oxygenase-1, NADP (H):quinone oxidoreductase in MCF-7/TAM cells was higher than that in MCF-7 cells. Epicatechin gallate (EGCG) significantly sensitizes MCF-7/TAM cells to tamoxifen and dramatically reduced Nrf2 expression at both the messenger RNA and protein, leading to a reduction of Nrf2-downstream genes. In addition, using siRNA technique, we found that the intracellular Nrf2 protein level was significantly decreased in MCF-7/TAM cells and tamoxifen resistance was partially reversed by Nrf2 siRNA. Combination of siRNA-directed gene silencing with EGCG downregulated the Nrf2-dependent response and partly reversed tamoxifen resistance in MCF-7/TAM cells in a synergic manner. These results suggested that combining the chemotherapeutic effect of EGCG with siRNA-mediated Nrf2 knock-down results in the feasibility of using Nrf2 inhibitors to increase efficacy of chemotherapeutic drugs.
Keywords: Apoptosis; Epigallocatechin-3-gallate; MCF-7 breast cancer; Nrf2 siRNA; Tamoxifen.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Drug resistance associates with activation of Nrf2 in MCF-7/DOX cells, and wogonin reverses it by down-regulating Nrf2-mediated cellular defense response.Mol Carcinog. 2013 Oct;52(10):824-34. doi: 10.1002/mc.21921. Epub 2012 May 16. Mol Carcinog. 2013. PMID: 22593043
-
(-)-Epigallocatechin-3-gallate down-regulates EGFR, MMP-2, MMP-9 and EMMPRIN and inhibits the invasion of MCF-7 tamoxifen-resistant cells.Biosci Rep. 2011 Apr;31(2):99-108. doi: 10.1042/BSR20090143. Biosci Rep. 2011. PMID: 20446926
-
Increased expression of Nrf2/ARE-dependent anti-oxidant proteins in tamoxifen-resistant breast cancer cells.Free Radic Biol Med. 2008 Aug 15;45(4):537-46. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2008.05.011. Epub 2008 May 24. Free Radic Biol Med. 2008. PMID: 18539158
-
The Role of the Nrf2/ARE Antioxidant System in Preventing Cardiovascular Diseases.Diseases. 2016 Nov 11;4(4):34. doi: 10.3390/diseases4040034. Diseases. 2016. PMID: 28933413 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interactions Between Natural Products and Tamoxifen in Breast Cancer: A Comprehensive Literature Review.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Jun 2;13:847113. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.847113. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35721162 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Involvement of Peroxiporins and Antioxidant Transcription Factors in Breast Cancer Therapy Resistance.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Dec 8;15(24):5747. doi: 10.3390/cancers15245747. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38136293 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cellular Stress Response (Hormesis) in Response to Bioactive Nutraceuticals with Relevance to Alzheimer Disease.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2023 Mar;38(7-9):643-669. doi: 10.1089/ars.2022.0214. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2023. PMID: 36656673 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Alleviation of Multidrug Resistance by Flavonoid and Non-Flavonoid Compounds in Breast, Lung, Colorectal and Prostate Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jan 8;21(2):401. doi: 10.3390/ijms21020401. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 31936346 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SOX2OT variant 7 contributes to the synergistic interaction between EGCG and Doxorubicin to kill osteosarcoma via autophagy and stemness inhibition.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2018 Feb 23;37(1):37. doi: 10.1186/s13046-018-0689-3. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2018. PMID: 29475441 Free PMC article.
-
NRF2 Modulators of Plant Origin and Their Ability to Overcome Multidrug Resistance in Cancers.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Oct 26;25(21):11500. doi: 10.3390/ijms252111500. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39519053 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

