Inflammasome activation in decompensated liver cirrhosis
- PMID: 26855691
- PMCID: PMC4733463
- DOI: 10.4254/wjh.v8.i4.207
Inflammasome activation in decompensated liver cirrhosis
Abstract
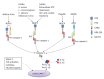
Inflammation participates in the pathogenesis of many liver diseases, including liver cirrhosis. Certain inflammatory citokines, such as interleukin (IL)-1β and IL-18, are produced after the activation of a multiprotein complex known as the inflammasome. Activation of the inflammasome has been documented in several liver diseases, but its role in the development and progression of liver cirrhosis or the complications associated with this disease is still largely unknown. We have recently studied the impact of the inflammasome in the sterile inflammatory response that takes place in the ascitic fluid of patients with decompensated cirrhosis, providing evidence that activation of the absent in melanoma 2 (AIM2) inflammasome is an important response in these patients. Ascitic fluid-derived macrophages were able to mount a very robust AIM2-mediated response even in the absence of a priming signal, which is usually required for the full activation of all the inflammasomes. In addition, high level of inflammasome activation in these patients was associated with a higher degree of liver disease and an increased incidence of spontaneous bacterial peritonitis. These results may help explain the exacerbated inflammatory response that usually occurs in patients with decompensated cirrhosis in the absence of detectable infections. Thus, inflammasomes should be considered as possible therapeutic targets in sterile inflammatory complications in patients with cirrhosis.
Keywords: Absent in melanoma 2; Ascites; Cirrhosis; Inflammasome; Interleukin-1β.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Absent in melanoma 2 triggers a heightened inflammasome response in ascitic fluid macrophages of patients with cirrhosis.J Hepatol. 2015 Jan;62(1):64-71. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2014.08.027. Epub 2014 Aug 27. J Hepatol. 2015. PMID: 25173967
-
The expression and activation of the AIM2 inflammasome correlates with inflammation and disease severity in patients with acute pancreatitis.Pancreatology. 2017 May-Jun;17(3):364-371. doi: 10.1016/j.pan.2017.03.006. Epub 2017 Mar 18. Pancreatology. 2017. PMID: 28342645
-
Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans-Induced AIM2 Inflammasome Activation Is Suppressed by Xylitol in Differentiated THP-1 Macrophages.J Periodontol. 2016 Jun;87(6):e116-26. doi: 10.1902/jop.2016.150477. Epub 2016 Feb 15. J Periodontol. 2016. PMID: 26876350
-
The absent in melanoma 2 (AIM2) inflammasome in microbial infection.Clin Chim Acta. 2019 Aug;495:100-108. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2019.04.052. Epub 2019 Apr 5. Clin Chim Acta. 2019. PMID: 30959045 Review.
-
The role of NLRP3 and AIM2 in inflammasome activation during Brucella abortus infection.Semin Immunopathol. 2017 Feb;39(2):215-223. doi: 10.1007/s00281-016-0581-1. Epub 2016 Jul 12. Semin Immunopathol. 2017. PMID: 27405866 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Bloodstream infection due to Escherichia coli in liver cirrhosis patients: clinical features and outcomes.Oncotarget. 2017 Dec 13;9(87):35780-35789. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.23200. eCollection 2018 Nov 6. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 30515269 Free PMC article.
-
Gut Microbiome-based Therapeutics in Liver Cirrhosis: Basic Consideration for the Next Step.J Clin Transl Hepatol. 2017 Sep 28;5(3):249-260. doi: 10.14218/JCTH.2017.00008. Epub 2017 Jun 29. J Clin Transl Hepatol. 2017. PMID: 28936406 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Melatonin prevents oxidative stress, inflammatory activity, and DNA damage in cirrhotic rats.World J Gastroenterol. 2022 Jan 21;28(3):348-364. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i3.348. World J Gastroenterol. 2022. PMID: 35110954 Free PMC article.
-
Microbiological Characteristics and Antibiotic Sensitivity in Patients with Nosocomial Spontaneous Bacterial Peritonitis Caused by Escherichia coli: A Multicenter Study.Infect Microbes Dis. 2020 Aug 7;2(4):167-172. doi: 10.1097/IM9.0000000000000035. eCollection 2020 Dec. Infect Microbes Dis. 2020. PMID: 38630105 Free PMC article.
-
NLRP3 inflammasome activation results in liver inflammation and fibrosis in mice infected with Schistosoma japonicum in a Syk-dependent manner.Sci Rep. 2017 Aug 14;7(1):8120. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-08689-1. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28808303 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Francés R, Zapater P, González-Navajas JM, Muñoz C, Caño R, Moreu R, Pascual S, Bellot P, Pérez-Mateo M, Such J. Bacterial DNA in patients with cirrhosis and noninfected ascites mimics the soluble immune response established in patients with spontaneous bacterial peritonitis. Hepatology. 2008;47:978–985. - PubMed
-
- González-Navajas JM, Bellot P, Francés R, Zapater P, Muñoz C, García-Pagán JC, Pascual S, Pérez-Mateo M, Bosch J, Such J. Presence of bacterial-DNA in cirrhosis identifies a subgroup of patients with marked inflammatory response not related to endotoxin. J Hepatol. 2008;48:61–67. - PubMed
-
- Zapater P, Francés R, González-Navajas JM, de la Hoz MA, Moreu R, Pascual S, Monfort D, Montoliu S, Vila C, Escudero A, et al. Serum and ascitic fluid bacterial DNA: a new independent prognostic factor in noninfected patients with cirrhosis. Hepatology. 2008;48:1924–1931. - PubMed
-
- Martinon F, Burns K, Tschopp J. The inflammasome: a molecular platform triggering activation of inflammatory caspases and processing of proIL-beta. Mol Cell. 2002;10:417–426. - PubMed
-
- Schroder K, Tschopp J. The inflammasomes. Cell. 2010;140:821–832. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

