In vivo subcellular resolution optical imaging in the lung reveals early metastatic proliferation and motility
- PMID: 26855844
- PMCID: PMC4737962
- DOI: 10.1080/21659087.2015.1086613
In vivo subcellular resolution optical imaging in the lung reveals early metastatic proliferation and motility
Abstract
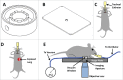
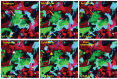
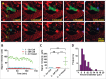
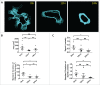
To better understand breast cancer metastatic cell seeding, we have employed multiphoton microscopy and a vacuum stabilized window which eliminates the need for complex registration software, video rate microscopy or specialized gating electronics to observe the initial steps of tumor cell seeding within the living, breathing lung. We observe that upon arrival to the lung, tumor cells are found exclusively in capillary vessels, completely fill their volume and display an initial high level of protrusive activity that dramatically reduces over time. Further, we observe a concomitant increase in positional stability during this same period. We employ several techniques accessible to most imaging labs for optimizing signal to noise and resolution which enable us to report the first direct observation, with subcellular resolution, of the arrival, proliferation, and motility of metastatic tumor cells within the lung.
Keywords: Intravital imaging; cancer; macrophage; metastasis; multiphoton; vacuum window.
Figures
References
-
- Mehlen P, Puisieux A. Metastasis: a question of life or death. Nat Rev Cancer 2006; 6:449-58; PMID:16723991; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1038/nrc1886 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Guth U, Magaton I, Huang DJ, Fisher R, Schötzau A, Vetter M. Primary and secondary distant metastatic breast cancer: two sides of the same coin. Breast 2014; 23:26-32; PMID:24215983; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1016/j.breast.2013.10.007 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Chambers AF, Groom AC, MacDonald IC. Dissemination and growth of cancer cells in metastatic sites. Nat Rev Cancer 2002; 2:563-72; PMID:12154349; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1038/nrc865 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Gligorijevic B, Bergman A, Condeelis J. Multiparametric classification links tumor microenvironments with tumor cell phenotype. PLoS Biol 2014; 12:e1001995; PMID:25386698; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1371/journal.pbio.1001995 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
