Quality gaps identified through mortality review
- PMID: 26856617
- PMCID: PMC5284344
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjqs-2015-004735
Quality gaps identified through mortality review
Abstract
Background: Hospital mortality rate is a common measure of healthcare quality. Morbidity and mortality meetings are common but there are few reports of hospital-wide mortality-review processes to provide understanding of quality-of-care problems associated with patient deaths.
Objective: To describe the implementation and results from an institution-wide mortality-review process.
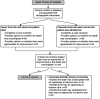
Design: A nurse and a physician independently reviewed every death that occurred at our multisite teaching institution over a 3-month period. Deaths judged by either reviewer to be unanticipated or to have any opportunity for improvement were reviewed by a multidisciplinary committee. We report characteristics of patients with unanticipated death or opportunity for improved care and summarise the opportunities for improved care.
Results: Over a 3-month period, we reviewed all 427 deaths in our hospital in detail; 33 deaths (7.7%) were deemed unanticipated and 100 (23.4%) were deemed to be associated with an opportunity for improvement. We identified 97 opportunities to improve care. The most common gap in care was: 'goals of care not discussed or the discussion was inadequate' (n=25 (25.8%)) and 'delay or failure to achieve a timely diagnosis' (n=8 (8.3%)). Patients who had opportunities for improvement had longer length of stay and a lower baseline predicted risk of death in hospital. Nurse and physician reviewers spent approximately 142 h reviewing cases outside of committee meetings.
Conclusions: Our institution-wide mortality review found many quality gaps among decedents, in particular inadequate discussion of goals of care.
Keywords: Chart review methodologies; Healthcare quality improvement; Hospital medicine; Quality measurement.
Published by the BMJ Publishing Group Limited. For permission to use (where not already granted under a licence) please go to http://www.bmj.com/company/products-services/rights-and-licensing/.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: None declared.
Figures
References
-
- Bird W. Thunder Bay hostpial death rates trending up: CIHI report. CBC News 2014 December 4th 2014.
-
- Press TC. Saskatoon hospital has the highest rate of in-facility deaths in Canada. The Gobe and Mail 2014 December 3rd.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous