The impact of chronic intermittent hypoxia on hematopoiesis and the bone marrow microenvironment
- PMID: 26856724
- PMCID: PMC4842224
- DOI: 10.1007/s00424-016-1797-6
The impact of chronic intermittent hypoxia on hematopoiesis and the bone marrow microenvironment
Abstract
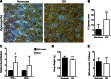
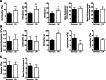
Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) is a highly prevalent sleep-related breathing disorder which is associated with patient morbidity and an elevated risk of developing hypertension and cardiovascular diseases. There is ample evidence for the involvement of bone marrow (BM) cells in the pathophysiology of cardiovascular diseases but a connection between OSA and modulation of the BM microenvironment had not been established. Here, we studied how chronic intermittent hypoxia (CIH) affected hematopoiesis and the BM microenvironment, in a rat model of OSA. We show that CIH followed by normoxia increases the bone marrow hypoxic area, increases the number of multipotent hematopoietic progenitors (CFU assay), promotes erythropoiesis, and increases monocyte counts. In the BM microenvironment of CIH-subjected animals, the number of VE-cadherin-expressing blood vessels, particularly sinusoids, increased, accompanied by increased smooth muscle cell coverage, while vWF-positive vessels decreased. Molecularly, we investigated the expression of endothelial cell-derived genes (angiocrine factors) that could explain the cellular phenotypes. Accordingly, we observed an increase in colony-stimulating factor 1, vascular endothelium growth factor, delta-like 4, and angiopoietin-1 expression. Our data shows that CIH induces vascular remodeling in the BM microenvironment, which modulates hematopoiesis, increasing erythropoiesis, and circulating monocytes. Our study reveals for the first time the effect of CIH in hematopoiesis and suggests that hematopoietic changes may occur in OSA patients.
Keywords: Bone marrow microenvironment; Chronic intermittent hypoxia; Hematopoiesis; Vascular niche.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Angiopoietin-like proteins 8 knockout reduces intermittent hypoxia-induced vascular remodeling in a murine model of obstructive sleep apnea.Biochem Pharmacol. 2021 Apr;186:114502. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2021.114502. Epub 2021 Mar 6. Biochem Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33684391
-
Sex-dependent effects of chronic intermittent hypoxia: implication for obstructive sleep apnea.Biol Sex Differ. 2024 Apr 25;15(1):38. doi: 10.1186/s13293-024-00613-3. Biol Sex Differ. 2024. PMID: 38664845 Free PMC article.
-
Hypoxic niche-mediated regeneration of hematopoiesis in the engraftment window is dominantly affected by oxygen tension in the milieu.Stem Cells Dev. 2015 Oct 15;24(20):2423-36. doi: 10.1089/scd.2015.0112. Epub 2015 Jul 28. Stem Cells Dev. 2015. PMID: 26107807 Free PMC article.
-
Obstructive sleep apnea and chronic intermittent hypoxia: a review.Chin J Physiol. 2006 Oct 31;49(5):234-43. Chin J Physiol. 2006. PMID: 17294831 Review.
-
Chronic intermittent hypoxia exposure-induced atherosclerosis: a brief review.Immunol Res. 2015 Dec;63(1-3):121-30. doi: 10.1007/s12026-015-8703-8. Immunol Res. 2015. PMID: 26407987 Review.
Cited by
-
Sleep apnea syndrome associated with gonadal hormone imbalance (Review).Biomed Rep. 2023 Oct 25;19(6):101. doi: 10.3892/br.2023.1683. eCollection 2023 Dec. Biomed Rep. 2023. PMID: 38025832 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Elucidating the combined effect of intermittent hypoxia training and acetazolamide on hypoxia induced hematological and physiological changes.Curr Res Physiol. 2022 Jul 18;5:327-337. doi: 10.1016/j.crphys.2022.07.004. eCollection 2022. Curr Res Physiol. 2022. PMID: 35880035 Free PMC article.
-
Nocturnal Mean Oxygen Saturation Is Associated with Secondary Polycythemia in Young Adults with Obstructive Sleep Apnea, Especially in Men.Nat Sci Sleep. 2019 Dec 5;11:377-386. doi: 10.2147/NSS.S226143. eCollection 2019. Nat Sci Sleep. 2019. PMID: 31824198 Free PMC article.
-
Obstructive Sleep Apnea, Hypoxia, and Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2019 Apr 1;199(7):830-841. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201806-1109TR. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2019. PMID: 30422676 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Long-Term Environmental Hypoxia Exposure and Haematopoietic Prolyl Hydroxylase-1 Deletion Do Not Impact Experimental Crohn's Like Ileitis.Biology (Basel). 2021 Sep 8;10(9):887. doi: 10.3390/biology10090887. Biology (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34571764 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bausero P, Ben-Mahdi M-H, Mazucatelli J-P, Bloy C, Perrot-Applanat M. Vascular endothelial growth factor is modulated in vascular muscle cells by estradiol, tamoxifen, and hypoxia. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2000;279:H2033–H2042. - PubMed
-
- Boyum A, Carsten AL, Laerum OD, Cronkite EP. Kinetics of cell proliferation of murine bone marrow cells cultured in diffusion chambers: effect of hypoxia, bleeding, erythropoietin injections, polycythemia, and irradiation of the host. Blood. 1972;40:174–188. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

