Comprehensive behavioral phenotyping of a new Semaphorin 3 F mutant mouse
- PMID: 26856818
- PMCID: PMC4746810
- DOI: 10.1186/s13041-016-0196-4
Comprehensive behavioral phenotyping of a new Semaphorin 3 F mutant mouse
Abstract
Background: Semaphorin 3 F (Sema3F) is a secreted type of the Semaphorin family of axon guidance molecules. Sema3F and its receptor neuropilin-2 (Npn-2) are expressed in a mutually exclusive manner in the embryonic mouse brain regions including olfactory bulb, hippocampus, and cerebral cortex. Sema3F is thought to have physiological functions in the formation of neuronal circuitry and its refinement. However, functional roles of Sema3F in the brain remain to be clarified. Here, we examined behavioral effects of Sema3F deficiency through a comprehensive behavioral test battery in Sema3F knockout (KO) male mice to understand the possible functions of Sema3F in the brain.
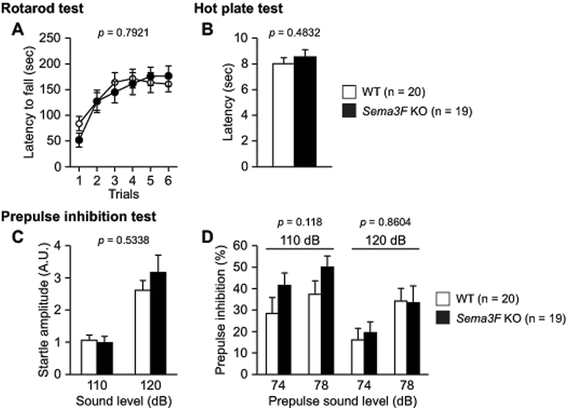
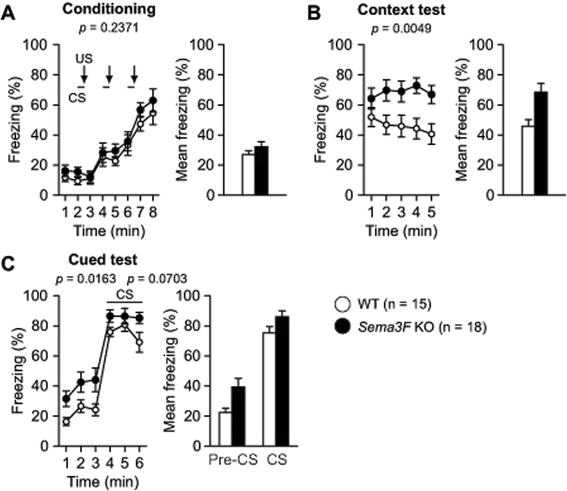
Results: Male Sema3F KO and wild-type (WT) control mice were subjected to a battery of behavioral tests, including neurological screen, rotarod, hot plate, prepulse inhibition, light/dark transition, open field, elevated plus maze, social interaction, Porsolt forced swim, tail suspension, Barnes maze, and fear conditioning tests. In the open field test, Sema3F KO mice traveled shorter distance and spent less time in the center of the field than WT controls during the early testing period. In the light/dark transition test, Sema3F KO mice also exhibited decreased distance traveled, fewer number of transitions, and longer latency to enter the light chamber compared with WT mice. In addition, Sema3F KO mice traveled shorter distance than WT mice in the elevated plus maze test, although there were no differences between genotypes in open arm entries and time spent in open arms. Similarly, Sema3F KO mice showed decreased distance traveled in the social interaction test. Sema3F KO mice displayed reduced immobility in the Porsolt forced swim test whereas there was no difference in immobility between genotypes in the tail suspension test. In the fear conditioning test, Sema3F KO mice exhibited increased freezing behavior when exposed to a conditioning context and an altered context in absence of a conditioned stimulus. In the tests for assessing motor function, pain sensitivity, startle response to an acoustic stimulus, sensorimotor gating, or spatial reference memory, there were no significant behavioral differences between Sema3F KO and WT mice.
Conclusions: These results suggest that Sema3F deficiency induces decreased locomotor activity and possibly abnormal anxiety-related behaviors and also enhances contextual memory and generalized fear in mice. Thus, our findings suggest that Sema3F plays important roles in the development of neuronal circuitry underlying the regulation of some aspects of anxiety and fear responses.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Comprehensive behavioral analysis of the Cdkl5 knockout mice revealed significant enhancement in anxiety- and fear-related behaviors and impairment in both acquisition and long-term retention of spatial reference memory.PLoS One. 2018 Apr 27;13(4):e0196587. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0196587. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 29702698 Free PMC article.
-
Age-related changes in behavior in C57BL/6J mice from young adulthood to middle age.Mol Brain. 2016 Jan 28;9:11. doi: 10.1186/s13041-016-0191-9. Mol Brain. 2016. PMID: 26822304 Free PMC article.
-
Age-related behavioral changes from young to old age in male mice of a C57BL/6J strain maintained under a genetic stability program.Neuropsychopharmacol Rep. 2019 Jun;39(2):100-118. doi: 10.1002/npr2.12052. Epub 2019 Feb 27. Neuropsychopharmacol Rep. 2019. PMID: 30816023 Free PMC article.
-
Behavioral profiles of inbred strains on novel olfactory, spatial and emotional tests for reference memory in mice.Genes Brain Behav. 2002 Jan;1(1):55-69. doi: 10.1046/j.1601-1848.2001.00005.x. Genes Brain Behav. 2002. PMID: 12886950 Review.
-
Altered fear circuits in 5-HT(1A) receptor KO mice.Biol Psychiatry. 2000 Dec 15;48(12):1157-63. doi: 10.1016/s0006-3223(00)01041-6. Biol Psychiatry. 2000. PMID: 11137057 Review.
Cited by
-
Effect of simultaneous testing of two mice in the tail suspension test and forced swim test.Sci Rep. 2022 Jun 2;12(1):9224. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-12986-9. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35654971 Free PMC article.
-
Behavioral alterations in long-term Toxoplasma gondii infection of C57BL/6 mice are associated with neuroinflammation and disruption of the blood brain barrier.PLoS One. 2021 Oct 5;16(10):e0258199. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0258199. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 34610039 Free PMC article.
-
Potential crosstalk between sonic hedgehog-WNT signaling and neurovascular molecules: Implications for blood-brain barrier integrity in autism spectrum disorder.J Neurochem. 2021 Oct;159(1):15-28. doi: 10.1111/jnc.15460. Epub 2021 Aug 6. J Neurochem. 2021. PMID: 34169527 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Behavioral effects of long-term oral administration of aluminum ammonium sulfate in male and female C57BL/6J mice.Neuropsychopharmacol Rep. 2018 Mar;38(1):18-36. doi: 10.1002/npr2.12002. Epub 2018 Feb 9. Neuropsychopharmacol Rep. 2018. PMID: 30106265 Free PMC article.
-
Functions of Plexins/Neuropilins and Their Ligands during Hippocampal Development and Neurodegeneration.Cells. 2019 Feb 28;8(3):206. doi: 10.3390/cells8030206. Cells. 2019. PMID: 30823454 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

