Long-term antihypertensive effects of far-infrared ray irradiated from wooden board in spontaneously hypertensive rats
- PMID: 26857237
- PMCID: PMC4745157
- DOI: 10.1186/s12906-016-1040-1
Long-term antihypertensive effects of far-infrared ray irradiated from wooden board in spontaneously hypertensive rats
Abstract
Background: Far-infrared ray (FIR) has been widely used in promoting health and has been shown to exert beneficial effects in vascular function. The non-thermal effect of FIR has been found to play a significant role in the protective effect on some vascular-related diseases, but its protective effects and use against hypertension have not been clearly presented.
Methods: In the present study, by using a wooden board coated with FIR-irradiated materials, we evaluated the long-term antihypertensive effect on spontaneously hypertensive rats (SHRs) in the environment in contact with the FIR-irradiated wooden board. SHRs were placed on the wooden board with or without FIR radiation for 4 weeks.
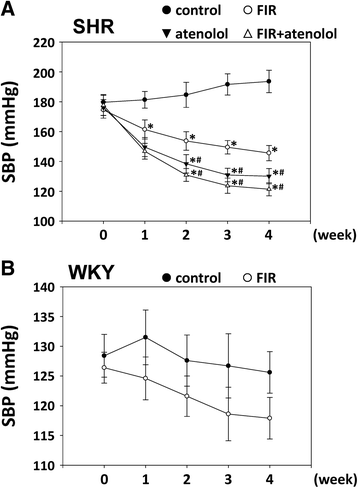
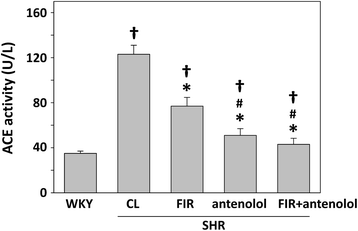
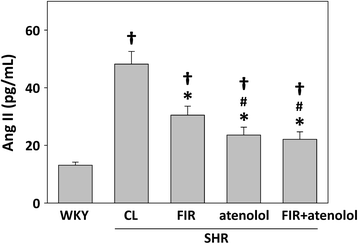
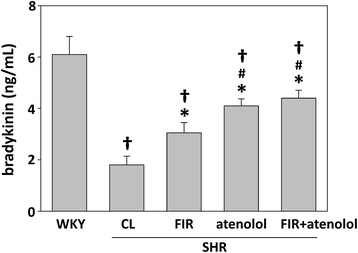
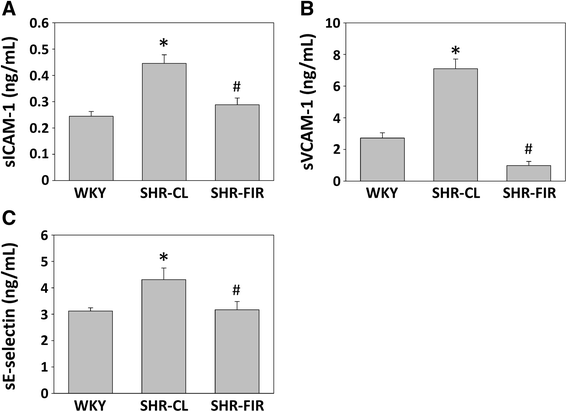
Results: The systolic blood pressure (BP) of SHRs undergoing different treatments was measured weekly using a tail-cuff method. FIR radiation significantly reduced the systolic BP of the SHRs along with a decreasing plasma level of angiotensin II and an increasing plasma level of bradykinin. In addition, long-term contact of FIR did not significantly affect the BP in normotensive Wistar Kyoto rats (WKYs).
Conclusions: Our results provided the evidence based on which FIR radiation could be considered an effective non-pharmacological choice for preventing hypertension.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Transient prehypertensive treatment in spontaneously hypertensive rats: a comparison of losartan and amlodipine regarding long-term blood pressure, cardiac and renal protection.Int J Mol Med. 2012 Dec;30(6):1376-86. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2012.1153. Epub 2012 Oct 9. Int J Mol Med. 2012. PMID: 23064712
-
Radiotelemetric evaluation of hemodynamic effects of long-term ethanol in spontaneously hypertensive and Wistar-Kyoto rats.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2000 Mar;292(3):944-51. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2000. PMID: 10688608
-
Low-dose angiotensin II reduces urinary cyclic AMP excretion in spontaneously hypertensive, but not normotensive, rats: independence from hypertension and renal hemodynamic effects of angiotensin.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1999 Oct;291(1):115-23. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1999. PMID: 10490894
-
Far-infrared radiation and its therapeutic parameters: A superior alternative for future regenerative medicine?Pharmacol Res. 2024 Oct;208:107349. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2024.107349. Epub 2024 Aug 14. Pharmacol Res. 2024. PMID: 39151679 Review.
-
Advances in far-infrared research: therapeutic mechanisms of disease and application in cancer detection.Lasers Med Sci. 2024 Jan 19;39(1):41. doi: 10.1007/s10103-024-03994-4. Lasers Med Sci. 2024. PMID: 38240851 Review.
Cited by
-
Far-Infrared-Emitting Sericite Board Upregulates Endothelial Nitric Oxide Synthase Activity through Increasing Biosynthesis of Tetrahydrobiopterin in Endothelial Cells.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2019 Oct 31;2019:1813282. doi: 10.1155/2019/1813282. eCollection 2019. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2019. PMID: 31781259 Free PMC article.
References
-
- van Vark LC, Bertrand M, Akkerhuis KM, Brugts JJ, Fox K, Mourad JJ, et al. Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors reduce mortality in hypertension: a meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials of renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system inhibitors involving 158,998 patients. Eur Heart J. 2012;33:2088–97. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehs075. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

