Association of Interferon Regulatory Factor-4 Polymorphism rs12203592 With Divergent Melanoma Pathways
- PMID: 26857527
- PMCID: PMC4948568
- DOI: 10.1093/jnci/djw004
Association of Interferon Regulatory Factor-4 Polymorphism rs12203592 With Divergent Melanoma Pathways
Abstract
Background: Solar elastosis and neval remnants are histologic markers characteristic of divergent melanoma pathways linked to differences in age at onset, host phenotype, and sun exposure. However, the association between these pathway markers and newly identified low-penetrance melanoma susceptibility loci remains unknown.
Methods: In the Genes, Environment and Melanoma (GEM) Study, 2103 Caucasian participants had first primary melanomas that underwent centralized pathology review. For 47 single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) previously identified as low-penetrant melanoma risk variants, we used multinomial logistic regression to compare melanoma with solar elastosis and melanoma with neval remnants simultaneously to melanoma with neither of these markers, excluding melanomas with both markers. All statistical tests were two-sided.
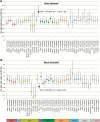
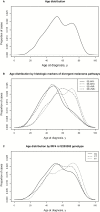
Results: IRF4 rs12203592 was the only SNP to pass the false discovery threshold in baseline models adjusted for age, sex, and study center. rs12203592*T was associated positively with melanoma with solar elastosis (odds ratio [OR] = 1.47, 95% confidence interval [CI] = 1.18 to 1.82) and inversely with melanoma with neval remnants (OR = 0.65, 95% CI = 0.48 to 0.87) compared with melanoma with neither marker (P global = 3.78 x 10(-08)). Adjusting for phenotypic characteristics and total sun exposure hours did not materially affect rs12203592's associations. Distinct early- and late-onset age distributions were observed in patients with IRF4 rs12203592 [CC] and [TT] genotypes, respectively.
Conclusions: Our findings suggest a role of IRF4 rs12203592 in pathway-specific risk for melanoma development. We hypothesize that IRF4 rs12203592 could underlie in part the bimodal age distribution reported for melanoma and linked to the divergent pathways.
© The Author 2016. Published by Oxford University Press. All rights reserved. For Permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Sun exposure and host phenotype as predictors of cutaneous melanoma associated with neval remnants or dermal elastosis.Int J Cancer. 2006 Aug 1;119(3):636-42. doi: 10.1002/ijc.21907. Int J Cancer. 2006. PMID: 16572428
-
Inherited Genetic Variants Associated with Melanoma BRAF/NRAS Subtypes.J Invest Dermatol. 2018 Nov;138(11):2398-2404. doi: 10.1016/j.jid.2018.04.025. Epub 2018 May 9. J Invest Dermatol. 2018. PMID: 29753029 Free PMC article.
-
Polymorphisms in nevus-associated genes MTAP, PLA2G6, and IRF4 and the risk of invasive cutaneous melanoma.Twin Res Hum Genet. 2011 Oct;14(5):422-32. doi: 10.1375/twin.14.5.422. Twin Res Hum Genet. 2011. PMID: 21962134 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic variants in PARP1 (rs3219090) and IRF4 (rs12203592) genes associated with melanoma susceptibility in a Spanish population.BMC Cancer. 2013 Mar 27;13:160. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-13-160. BMC Cancer. 2013. PMID: 23537197 Free PMC article.
-
Vitamin D receptor FokI, BsmI, TaqI, ApaI, and EcoRV polymorphisms and susceptibility to melanoma: a meta-analysis.J BUON. 2015 Jan-Feb;20(1):235-43. J BUON. 2015. PMID: 25778322 Review.
Cited by
-
Association of Inherited Genetic Variants with Multiple Primary Melanoma.Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2025 May 2;34(5):805-814. doi: 10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-24-1442. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2025. PMID: 40036058
-
Association of Melanoma-Risk Variants with Primary Melanoma Tumor Prognostic Characteristics and Melanoma-Specific Survival in the GEM Study.Curr Oncol. 2021 Nov 16;28(6):4756-4771. doi: 10.3390/curroncol28060401. Curr Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34898573 Free PMC article.
-
The Complex Interplay between Nevi and Melanoma: Risk Factors and Precursors.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Feb 10;24(4):3541. doi: 10.3390/ijms24043541. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36834954 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Defining Cancer Subtypes With Distinctive Etiologic Profiles: An Application to the Epidemiology of Melanoma.J Am Stat Assoc. 2017;112(517):54-63. doi: 10.1080/01621459.2016.1191499. Epub 2017 May 3. J Am Stat Assoc. 2017. PMID: 28603323 Free PMC article.
-
Disease-Associated Risk Variants in ANRIL Are Associated with Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocyte Presence in Primary Melanomas in the Population-Based GEM Study.Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2021 Dec;30(12):2309-2316. doi: 10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-21-0686. Epub 2021 Oct 4. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2021. PMID: 34607836 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Diepgen T, Mahler V. The epidemiology of skin cancer. Br J Dermatol. 2002;146(s61):1–6. - PubMed
-
- Garbe C, Leiter U. Melanoma epidemiology and trends. Clin Dermatol. 2009;27(1):3–9. - PubMed
-
- Kvaskoff M, Pandeya N, Green AC, et al. Solar elastosis and cutaneous melanoma: A site-specific analysis. Int J Cancer. 2015;136(12):2900–2911. - PubMed
-
- Whiteman DC, Watt P, Purdie DM, et al. Melanocytic nevi, solar keratoses, and divergent pathways to cutaneous melanoma. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2003;95(11):806–812. - PubMed
-
- Lee EY, Williamson R, Watt P, et al. Sun exposure and host phenotype as predictors of cutaneous melanoma associated with neval remnants or dermal elastosis. Int J Cancer. 2006;119(3):636–642. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P30 ES010126/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA083180/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA112524/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA016086/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA014089/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA098438/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30CA008748/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA112243/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30CA016086/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA098438/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01CA112243-05S1/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01CA83180/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01CA112243/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01CA112524-05S2/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA163251/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30CA014089/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA008748/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R33CA10704339/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30ES010126/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- R01CA112524/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

