Expression of multiple Bacillus subtilis genes is controlled by decay of slrA mRNA from Rho-dependent 3' ends
- PMID: 26857544
- PMCID: PMC4838369
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkw069
Expression of multiple Bacillus subtilis genes is controlled by decay of slrA mRNA from Rho-dependent 3' ends
Abstract
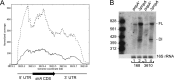
Timely turnover of RNA is an important element in the control of bacterial gene expression, but relatively few specific targets of RNA turnover regulation are known. Deletion of the Bacillus subtilis pnpA gene, encoding the major 3' exonuclease turnover enzyme, polynucleotide phosphorylase (PNPase), was shown previously to cause a motility defect correlated with a reduced level of the 32-gene fla/che flagellar biosynthesis operon transcript.fla/che operon transcript abundance has been shown to be inhibited by an excess of the small regulatory protein, SlrA, and here we find that slrA mRNA accumulated in the pnpA-deletion mutant. Mutation of slrA was epistatic to mutation of pnpA for the motility-related phenotype. Further, Rho-dependent termination was required for PNPase turnover of slrA mRNA. When the slrA gene was provided with a Rho-independent transcription terminator, gene regulation was no longer PNPase-dependent. Thus we show that the slrA transcript is a direct target of PNPase and that regulation of RNA turnover is a major determinant of motility gene expression. The interplay of specific transcription termination and mRNA decay mechanisms suggests selection for fine-tuning of gene expression.
© The Author(s) 2016. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures



References
-
- Lehnik-Habrink M., Schaffer M., Mader U., Diethmaier C., Herzberg C., Stulke J. RNA processing in Bacillus subtilis: identification of targets of the essential RNase Y. Mol. Microbiol. 2011;81:1459–1473. - PubMed
-
- Daou-Chabo R., Mathy N., Benard L., Condon C. Ribosomes initiating translation of the hbs mRNA protect it from 5′-to-3′ exoribonucleolytic degradation by RNase J1. Mol. Microbiol. 2009;71:1538–1550. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

