Porcine aminopeptidase N binds to F4+ enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli fimbriae
- PMID: 26857562
- PMCID: PMC4746772
- DOI: 10.1186/s13567-016-0313-5
Porcine aminopeptidase N binds to F4+ enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli fimbriae
Abstract
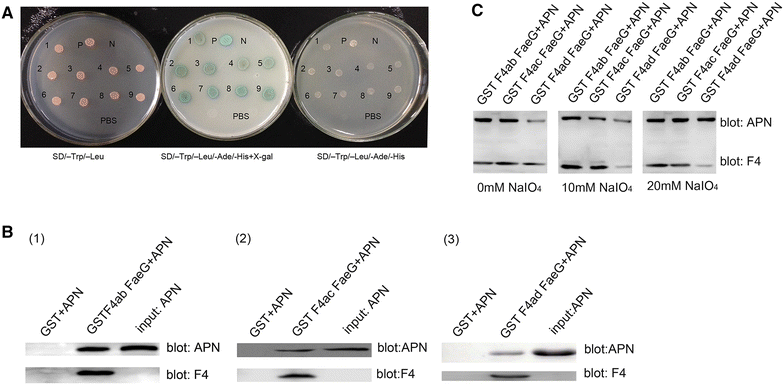
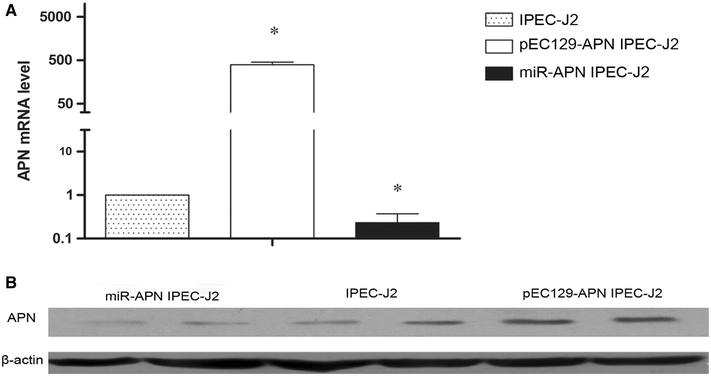
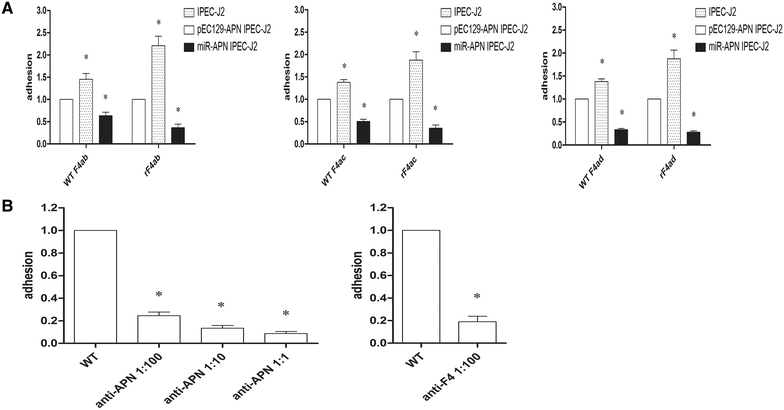
F4(+) enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (ETEC) strains cause diarrheal disease in neonatal and post-weaned piglets. Several different host receptors for F4 fimbriae have been described, with porcine aminopeptidase N (APN) reported most recently. The FaeG subunit is essential for the binding of the three F4 variants to host cells. Here we show in both yeast two-hybrid and pulldown assays that APN binds directly to FaeG, the major subunit of F4 fimbriae, from three serotypes of F4(+) ETEC. Modulating APN gene expression in IPEC-J2 cells affected ETEC adherence. Antibodies raised against APN or F4 fimbriae both reduced ETEC adherence. Thus, APN mediates the attachment of F4(+) E. coli to intestinal epithelial cells.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Binding determinants in the interplay between porcine aminopeptidase N and enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli F4 fimbriae.Vet Res. 2018 Feb 26;49(1):23. doi: 10.1186/s13567-018-0519-9. Vet Res. 2018. PMID: 29482635 Free PMC article.
-
Structural insight in the inhibition of adherence of F4 fimbriae producing enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli by llama single domain antibodies.Vet Res. 2015 Feb 24;46:14. doi: 10.1186/s13567-015-0151-x. Vet Res. 2015. PMID: 25828907 Free PMC article.
-
Mapping the Neutralizing Epitopes of Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli K88 (F4) Fimbrial Adhesin and Major Subunit FaeG.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2019 May 16;85(11):e00329-19. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00329-19. Print 2019 Jun 1. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 30926730 Free PMC article.
-
Receptor for the F4 fimbriae of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (ETEC).Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2015 Jun;99(12):4953-9. doi: 10.1007/s00253-015-6643-9. Epub 2015 May 13. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2015. PMID: 25967654 Review.
-
The F4 fimbrial antigen of Escherichia coli and its receptors.Vet Microbiol. 2000 Feb;71(3-4):223-44. doi: 10.1016/s0378-1135(99)00174-1. Vet Microbiol. 2000. PMID: 10703706 Review.
Cited by
-
Deletion of FaeG alleviated Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli F4ac-induced apoptosis in the intestine.AMB Express. 2021 Mar 18;11(1):44. doi: 10.1186/s13568-021-01201-z. AMB Express. 2021. PMID: 33738650 Free PMC article.
-
Production of porcine aminopeptidase N (pAPN) site-specific edited pigs.Anim Sci J. 2019 Mar;90(3):366-371. doi: 10.1111/asj.13163. Epub 2019 Jan 8. Anim Sci J. 2019. PMID: 30623527 Free PMC article.
-
Preparation and Evaluation of Novel Epitope-Based ETEC K88-K99 Bivalent Vaccine.Vet Sci. 2025 Apr 18;12(4):381. doi: 10.3390/vetsci12040381. Vet Sci. 2025. PMID: 40284883 Free PMC article.
-
Zinc uptake system ZnuACB is essential for maintaining pathogenic phenotype of F4ac+ enterotoxigenic E. coli (ETEC) under a zinc restricted environment.Vet Res. 2020 Oct 7;51(1):127. doi: 10.1186/s13567-020-00854-1. Vet Res. 2020. PMID: 33028391 Free PMC article.
-
Binding determinants in the interplay between porcine aminopeptidase N and enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli F4 fimbriae.Vet Res. 2018 Feb 26;49(1):23. doi: 10.1186/s13567-018-0519-9. Vet Res. 2018. PMID: 29482635 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

