XerC Contributes to Diverse Forms of Staphylococcus aureus Infection via agr-Dependent and agr-Independent Pathways
- PMID: 26857575
- PMCID: PMC4807471
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.01462-15
XerC Contributes to Diverse Forms of Staphylococcus aureus Infection via agr-Dependent and agr-Independent Pathways
Abstract
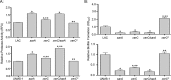
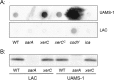
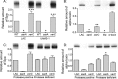
We demonstrate that mutation of xerC, which reportedly encodes a homologue of an Escherichia coli recombinase, limits biofilm formation in the methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus strain LAC and the methicillin-sensitive strain UAMS-1. This was not due to the decreased production of the polysaccharide intracellular adhesin (PIA) in either strain because the amount of PIA was increased in a UAMS-1xerC mutant and undetectable in both LAC and its isogenic xerC mutant. Mutation of xerC also resulted in the increased production of extracellular proteases and nucleases in both LAC and UAMS-1, and limiting the production of either class of enzymes increased biofilm formation in the isogenic xerC mutants. More importantly, the limited capacity to form a biofilm was correlated with increased antibiotic susceptibility in both strains in the context of an established biofilm in vivo. Mutation of xerC also attenuated virulence in a murine bacteremia model, as assessed on the basis of the bacterial loads in internal organs and overall lethality. It also resulted in the decreased accumulation of alpha toxin and the increased accumulation of protein A. These findings suggest that xerC may impact the functional status of agr. This was confirmed by demonstrating the reduced accumulation of RNAIII and AgrA in LAC and UAMS-1xerC mutants. However, this cannot account for the biofilm-deficient phenotype of xerC mutants because mutation of agr did not limit biofilm formation in either strain. These results demonstrate that xerC contributes to biofilm-associated infections and acute bacteremia and that this is likely due to agr-independent and -dependent pathways, respectively.
Copyright © 2016, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Limiting protease production plays a key role in the pathogenesis of the divergent clinical isolates of Staphylococcus aureus LAC and UAMS-1.Virulence. 2021 Dec;12(1):584-600. doi: 10.1080/21505594.2021.1879550. Virulence. 2021. PMID: 33538230 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of Staphylococcus aureus regulatory mutations that modulate biofilm formation in the USA300 strain LAC on virulence in a murine bacteremia model.Virulence. 2017 Nov 17;8(8):1776-1790. doi: 10.1080/21505594.2017.1373926. Epub 2017 Oct 4. Virulence. 2017. PMID: 28910576 Free PMC article.
-
Interconnections between Sigma B, agr, and proteolytic activity in Staphylococcus aureus biofilm maturation.Infect Immun. 2009 Apr;77(4):1623-35. doi: 10.1128/IAI.01036-08. Epub 2009 Feb 2. Infect Immun. 2009. PMID: 19188357 Free PMC article.
-
Methicillin resistance and the biofilm phenotype in Staphylococcus aureus.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2015 Jan 28;5:1. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2015.00001. eCollection 2015. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 25674541 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Quorum sensing-mediated regulation of staphylococcal virulence and antibiotic resistance.Future Microbiol. 2014;9(5):669-81. doi: 10.2217/fmb.14.31. Future Microbiol. 2014. PMID: 24957093 Review.
Cited by
-
Preliminary study on the effect of brazilin on biofilms of Staphylococcus aureus.Exp Ther Med. 2018 Sep;16(3):2108-2118. doi: 10.3892/etm.2018.6403. Epub 2018 Jul 4. Exp Ther Med. 2018. PMID: 30186447 Free PMC article.
-
Suppression of Alternative Lipooligosaccharide Glycosyltransferase Activity by UDP-Galactose Epimerase Enhances Murine Lung Infection and Evasion of Serum IgM.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2019 May 15;9:160. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2019.00160. eCollection 2019. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31157175 Free PMC article.
-
Limiting protease production plays a key role in the pathogenesis of the divergent clinical isolates of Staphylococcus aureus LAC and UAMS-1.Virulence. 2021 Dec;12(1):584-600. doi: 10.1080/21505594.2021.1879550. Virulence. 2021. PMID: 33538230 Free PMC article.
-
Global Screening of Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhimurium Genes for Desiccation Survival.Front Microbiol. 2017 Sep 8;8:1723. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.01723. eCollection 2017. Front Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28943871 Free PMC article.
-
The Impacts of msaABCR on sarA-Associated Phenotypes Are Different in Divergent Clinical Isolates of Staphylococcus aureus.Infect Immun. 2020 Jan 22;88(2):e00530-19. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00530-19. Print 2020 Jan 22. Infect Immun. 2020. PMID: 31740526 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Laabei M, Uhlemann AC, Lowy FD, Austin ED, Yokoyama M, Ouadi K, Feil E, Thorpe HA, Williams B, Perkins M, Peacock SJ, Clarke SR, Dordel J, Holden M, Votintseva AA, Bowden R, Crook DW, Young BC, Wilson DJ, Recker M, Massey RC. 2015. Evolutionary trade-offs underlie the multi-faceted virulence of Staphylococcus aureus. PLoS Biol 13:e1002229. doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.1002229. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

