Involvement of Endocannabinoids in Alcohol "Binge" Drinking: Studies of Mice with Human Fatty Acid Amide Hydrolase Genetic Variation and After CB1 Receptor Antagonists
- PMID: 26857901
- PMCID: PMC4962692
- DOI: 10.1111/acer.12989
Involvement of Endocannabinoids in Alcohol "Binge" Drinking: Studies of Mice with Human Fatty Acid Amide Hydrolase Genetic Variation and After CB1 Receptor Antagonists
Abstract
Background: The endocannabinoid system has been found to play an important role in modulating alcohol intake. Inhibition or genetic deletion of fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH; a key catabolic enzyme for endocannabinoids) leads to increased alcohol consumption and preference in rodent models. A common human single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP; C385A, rs324420) in the FAAH gene is associated with decreased enzymatic activity of FAAH, resulting in increased anandamide levels in both humans and FAAH C385A knock-in mice.
Methods: As this FAAH SNP has been reported to be associated with altered alcohol abuse, the present study used these genetic knock-in mice containing the human SNP C385A to determine the impact of variant FAAH gene on alcohol "binge" drinking in the drinking-in-the-dark (DID) model.
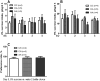
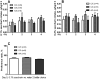
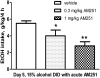
Results: We found that the FAAH(A/A) mice had greater alcohol intake and preference than the wild-type FAAH(C/C) mice, suggesting that increased endocannabinoid signaling in FAAH(A/A) mice led to increased alcohol "binge" consumption. The specificity on alcohol vulnerability was suggested by the lack of any FAAH genotype difference on sucrose or saccharin intake. Using the "binge" DID model, we confirmed that selective CB1 receptor antagonist AM251 reduced alcohol intake in the wild-type mice.
Conclusions: These data suggest that there is direct and selective involvement of the human FAAH C385A SNP and CB1 receptors in alcohol "binge" drinking.
Keywords: Alcohol Drinking; CB1 Receptor; Endocannabinoid System; Human Fatty Acid Amide Hydrolase C385A Knock-In.
Copyright © 2016 by the Research Society on Alcoholism.
Figures

References
-
- Arnone M, Maruani J, Chaperon F, Thiebot MH, Poncelet M, Soubrie P, Le Fur G. Selective inhibition of sucrose and ethanol intake by SR 141716, an antagonist of central cannabinoid (CB1) receptors. Psychopharmacology (Berlin) 1997;132:104–106. - PubMed
-
- Basavarajappa BS, Yalamanchili R, Cravatt BF, Cooper TB, Hungund BL. Increased ethanol consumption and preference and decreased ethanol sensitivity in female FAAH knockout mice. Neuropharmacology. 2006;50:834–844. - PubMed
-
- Blednov YA, Cravatt BF, Boehm SL, 2nd, Walker D, Harris RA. Role of endocannabinoids in alcohol consumption and intoxication: studies of mice lacking fatty acid amide hydrolase. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2007;32:1570–1582. - PubMed
-
- Bühler KM, Huertas E, Echeverry-Alzate V, Giné E, Moltó E, Montoliu L, López-Moreno JA. Risky alcohol consumption in young people is associated with the fatty acid amide hydrolase gene polymorphism C385A and affective rating of drug pictures. Mol Genet Genomics. 2014;289:279–89. - PubMed
-
- Chiang KP, Gerber AL, Sipe JC, Cravatt BF. Reduced cellular expression and activity of the P129T mutant of human fatty acid amide hydrolase: evidence for a link between defects in the endocannabinoid system and problem drug use. Hum Mol Genet. 2004;13:2113–2119. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

